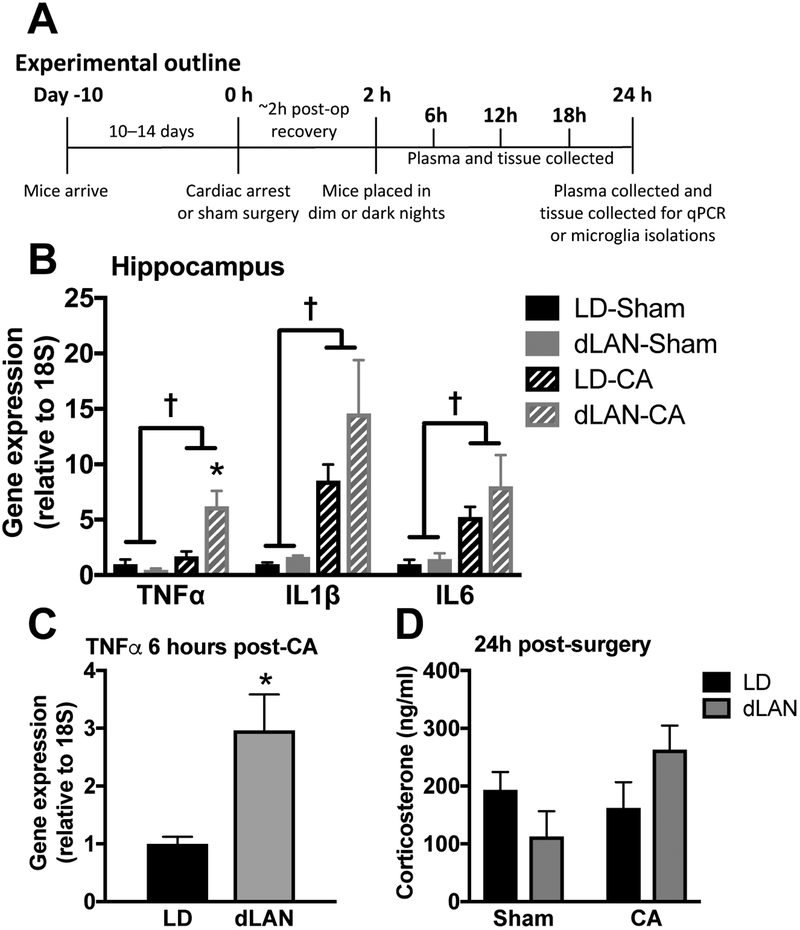
Figure 2. CA-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine elevations are exacerbated in the hippocampus of dLAN mice.
(a) Outline for experiments in figure 2 (n = 6 – 8/group; see supplemental table 1). (b) Hippocampal TNFα, IL1β, and IL6 mRNA concentrations are increased 24 h following CA relative to sham; furthermore, TNFα expression is potentiated by exposure to dLAN as compared to LD following CA in mice. (c) TNFα expression is elevated as early as 6 hours post-CA in the CA-dLAN group versus the CA-LD group (n = 4/group), this time point coincides with ~4 hours of exposure to dLAN. (d) Serum corticosterone concentrations at 24h were not altered by either CA or light at night (n = 6 – 8/group). There were no significant group differences in IL1β or IL6 at this early time point. Gene expression was assessed via RT-PCR and is presented as fold increase relative to a housekeeping gene (18S). The data are graphed as mean±SEM; a dagger symbol represents a significant main effect (p<0.05) between sham and CA, while an asterisk indicates a significant difference (p<0.05) between CA-LD and CA-dLAN.