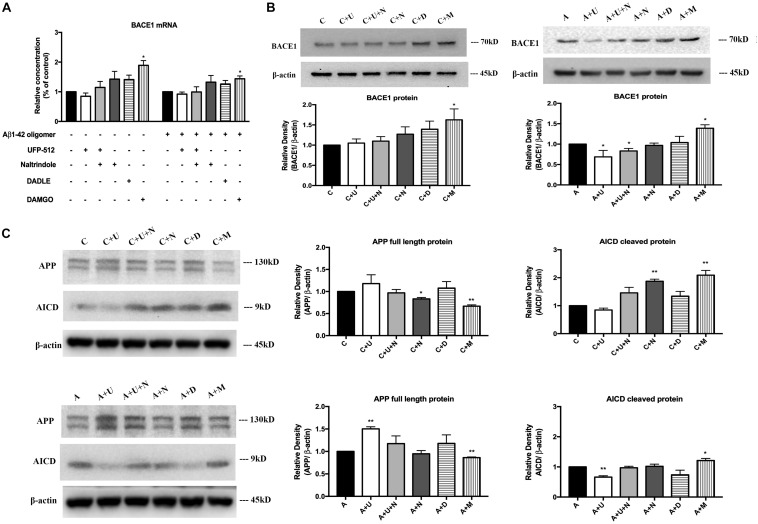
FIGURE 4.
DOR activation down-regulated, but MOR activation up-regulated BACE1 expression for APP processing. BACE1 mRNA and proteins were measured in the PC12 cells in the conditions of normal control and Aβ1–42 injury (48 h). APP processing was evaluated by measuring APP full length protein and AICD. N = 3 in each group. *p < 0.05, **p<0.01 vs. (C) or (A). (A) DAMGO-induced alternations in BACE1 mRNA in physiological condition and AD injury. (B) DAMGO-induced upregulation of BACE1 protein in both physiological condition and AD injury, while DOR activation specifically attenuated BACE1 expression under AD injury. (C) APP cleavage was associated with DOR activation and inhibition, while MOR activation significantly accelerated APP processing. Note that DOR activation had no significant effect on BACE1 mRNA expression though it tended to induce a slight reduction in both physiological and Aβ1–42 oligomer conditions. However, it significantly reduced the level of BACE1 protein in AD condition (Aβ1–42 oligomer exposure), which could be largely reversed by DOR antagonist naltrindole. In contrast, MOR activation with DAMGO significantly increased the expression of both BACE1 mRNA and protein in both physiological and Aβ1–42 oligomer conditions. Consistently, the APP cleavage was seriously interfered by DOR activation in Aβ1–42 oligomer conditions, while DAMGO accelerated APP processing in both physiological and Aβ1–42 oligomer conditions with a significant decrease in APP full length protein and a large increase in AICD, the APP cleavage product.