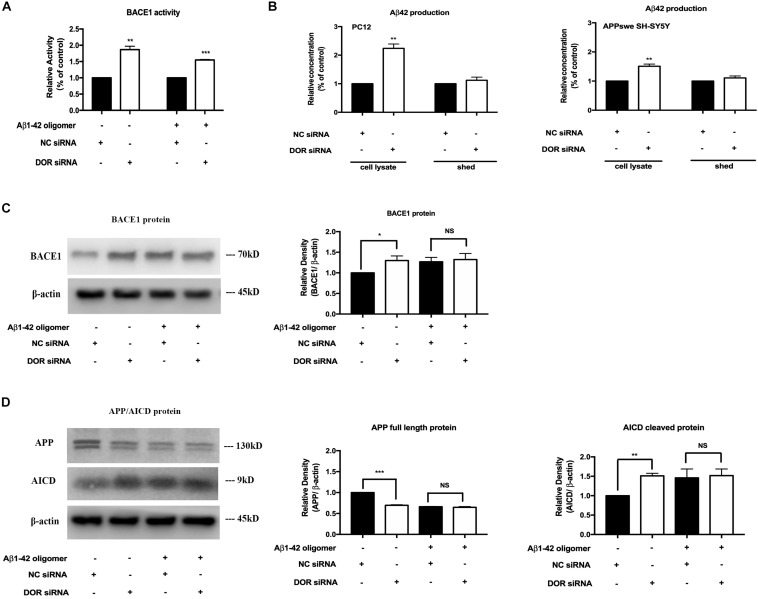
FIGURE 5.
Knocking-down DOR greatly enhanced BACE1 activity and expression for abnormal APP cleavage and contributed to the Aβ42 production. The PC12 cells transfected with DOR siRNA or negative control siRNA were cultured in the conditions of normal control and Aβ1–42 oligomer for 48 h. Similarly, APPswe SH-SY5Y cells were also transfected with human DOR siRNA or negative control siRNA for Aβ42 measurement. N = 3 in each group. NS: not significant, *p < 0.05 vs. (C) or (A); **p < 0.01 vs. (C) or (A); ***p < 0.001 vs. (C) or (A). (A) BACE1 activity before and after DOR knockdown. Note that DOR knockdown significantly increased BACE1 activities in both normal and AD conditions. (B) DOR knockdown induced effects on Aβ42 production and release in PC12 and APPswe SH-SY5Y cell models. DOR knockdown caused a sharp increase in the Aβ42 level production in the cell lysate, but not in the medium shed in PC12 cells and the same was true in APPswe SH-SY5Y cell model. (C) BACE1 expression was largely increased by DOR knockdown in physiological condition but not under Aβ1–42 injury. Note that DOR knockdown up-regulated BACE1 protein in physiological condition, but did not further increase BACE1 protein in the cells exposed to Aβ1–42 olimoger that already had an increased BACE1 protein. (D) DOR knockdown was associated with a rise in APP processing. Note that along with an increase in BACE1 expression after DOR knockdown, the transfection with DOR siRNA also significantly increased APP cleavage in the physiological condition. Aβ1–42 olimoger caused a quick cleavage of APP, which was not further enhanced by DOR knockdown.