Fig. 1: DMARCM technique.
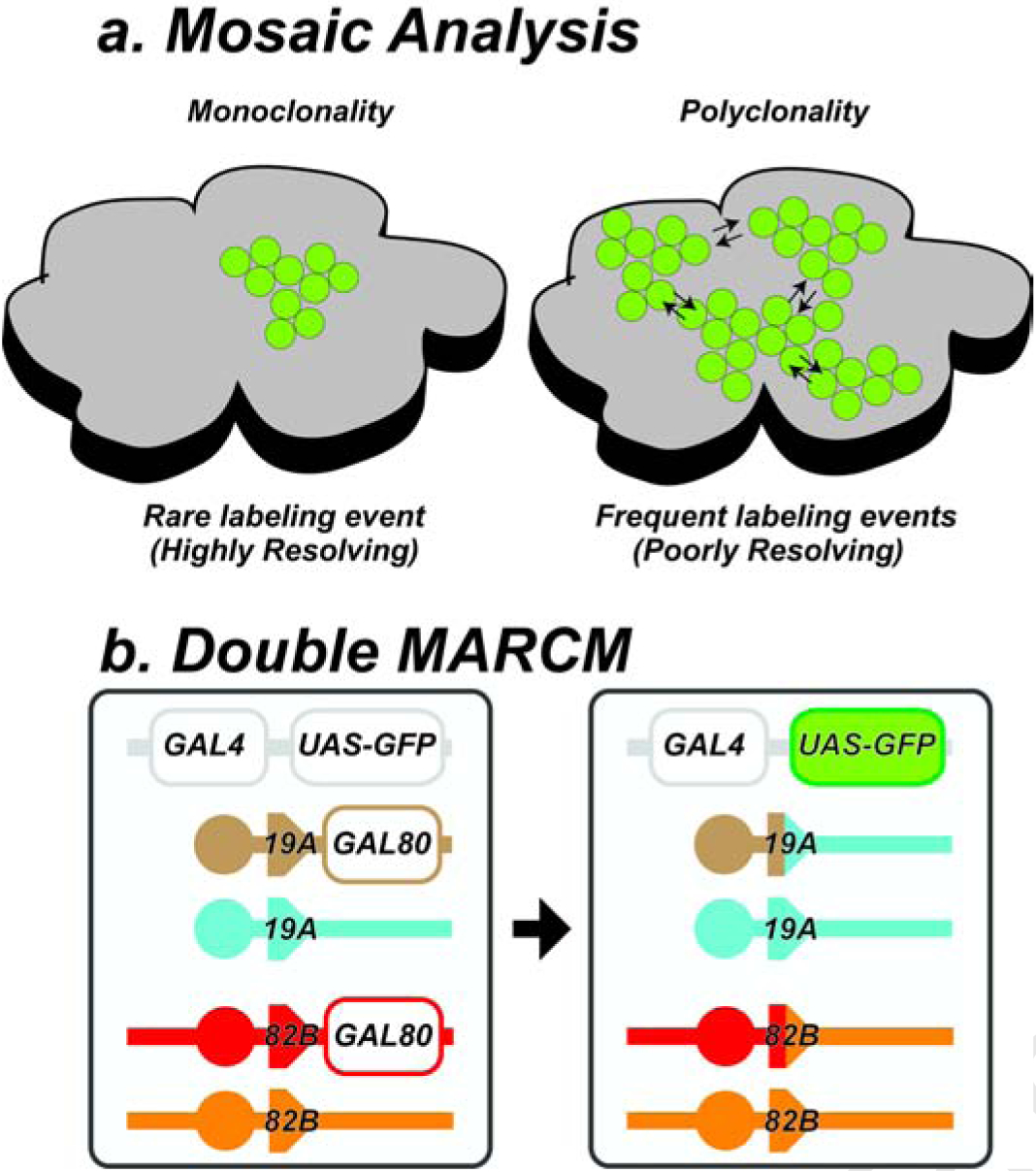
a, Cell labeling using genetic mosaic analysis. Rare labeling events produce high fidelity monoclonal maps of single cell lineages. Frequent labeling events produce polyclones. b, DMARCM strains contain two pairs of FRT sites. For example, a pair of FRT sites on the X chromosome (FRT19A) and second a pair on the right arm of the third chromosome (FRT82B), shown here on the left prior to DNA replication. Labeling induction promotes mitotic recombination between FRT sites on non-sister chromatids. Subsequent G2-X segregation generates a daughter cell lacking both copies of the tubGAL80 repressor, as shown on the right, leading to heritable expression of UAS-GFP under tub-GAL4 control.
