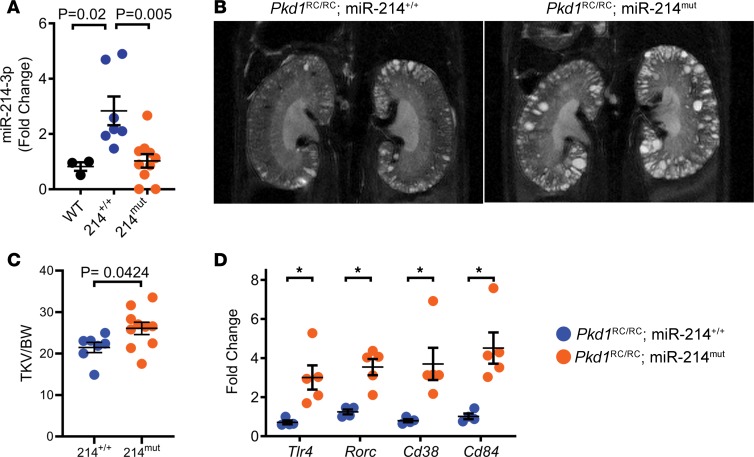
Figure 6. miR-214 deletion aggravates cyst growth in the Pkd1RC/RC model of ADPKD.
The role of miR-214 was studied in a second ADPKD mouse model. miR-214–/– mice were bred with Pkd1RC/RC mice to generate Pkd1RC/RC mice (n = 7) and Pkd1RC/RC miR-214mut mice (n = 10) with deletion of either one (n = 8) or both alleles (n = 2) of miR-214. (A) Q-PCR analysis showed that compared with kidneys from WT mice (black circles, n = 3), miR-214 expression was increased in kidneys of 140-day-old Pkd1RC/RC mice (blue circles). miR-214 expression was reduced in kidneys of Pkd1RC/RC miR-214mut (orange circles) compared with Pkd1RC/RC mice (blue circles). (B) MRI was performed to determine total kidney volume of Pkd1RC/RC mice (N = 7) and Pkd1RC/RC miR-214mut mice (N = 10) at 16 weeks of age. Representative MRI images corresponding to the mean of each group are shown. (C) Total kidney volume (TKV) normalized to BW was increased in Pkd1RC/RC miR-214mut mice compared with Pkd1RC/RC mice. (D) Q-PCR analysis showing upregulation of miR-214 target genes, Tlr4, Rorc, Cd38, and Cd84, in kidneys of 140-day-old Pkd1RC/RC miR-214mut mice (N = 5) compared with Pkd1RC/RC mice (N = 4). *P < 0.05; 1-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test (A); Student’s unpaired t test (C and D); error bars indicate SEM.