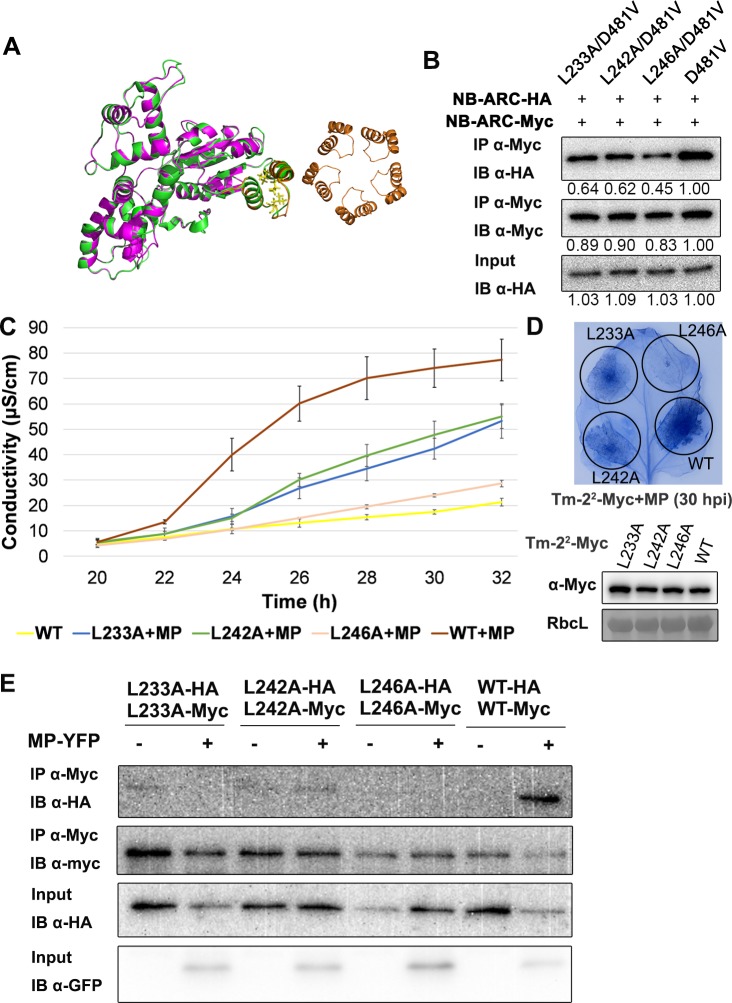
Fig 7. Tm-22 requires NB-ARC self-association for its function.
(A) Structure modeling of Tm-22 NB-ARC domain. Green, the predicted structure of Tm-22 NB-ARC domain; purple, the structure of ZAR1 (PDB ID: 6J5T); Orange, helix-loop-helix located at the center of ZAR1 inter-subunit-interface. Right orange ring shows the indicated helix-loop-helix motifs among the ZAR1 pentamer center [14]. (B) Potential oligomer surface mutations L233A, L242A and L246A weakened the self-association of NB-ARC (D481V). Numbers below the panel indicate the relative intensity analyzed by ImageJ. Indicated protein samples were subjected to IP with anti-Myc beads, followed by IB with anti-Myc or anti-HA antibody. (C) Ion leakage measurement showed L233A, L242A and L246A weakend full-length Tm-22 mediated cell death in the presence of TMV MP. The error bar indicates the standard deviation from 3 technical repetitions. The experiment was performed at least three times with similar results. (D) Trypan blue staining of infiltrated leaves collected at 30 hpi showed that for full-length proteins, L233A, L242A and L246A mutations weakened the cell death triggered by Tm-22/MP. The expression of Tm-22 and its mutants were detected by anti-Myc antibody. RbcL was stained by Ponceau S as loading control. (E) L233A, L242A and L246A mutations weakened TMV MP induced full-length Tm-22 self-association. Indicated protein samples were subjected to IP with anti-Myc beads, followed by IB with anti-Myc, anti-HA or anti-GFP antibody.