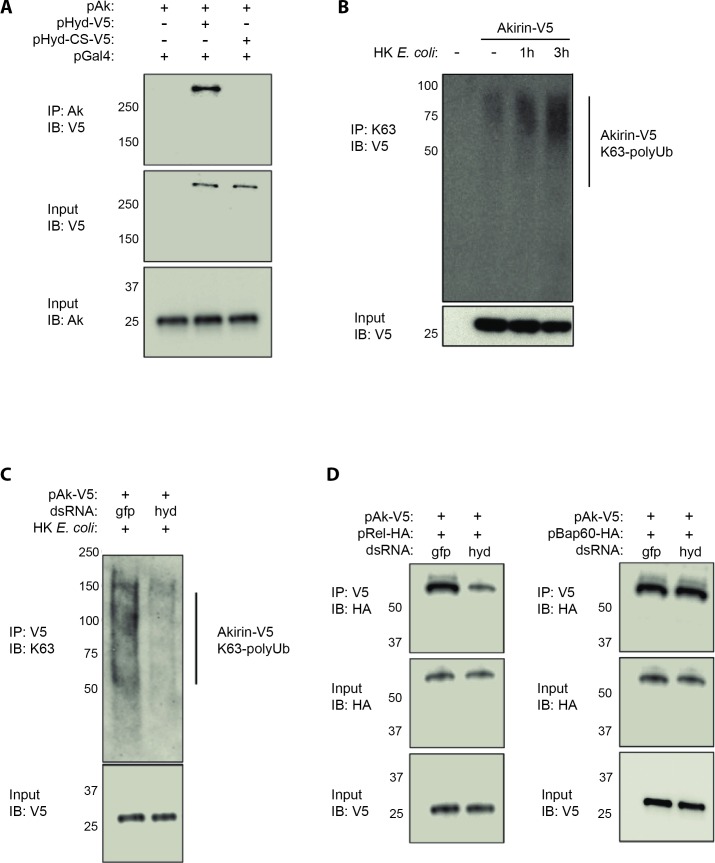
Fig 3. Hyd mediated-ubiquitination of Akirin is necessary for interaction with Relish.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation assay between over-expressed Akirin and Hyd in S2 cells. The cells were transiently transfected with Akirin, Gal4, Hyd-V5 and/or Hyd-CS-V5 expressing plasmids. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Akirin coupled agarose beads. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-V5 or anti-Akirin antibodies. (B) Immunoprecipitation assay of K63-polyUb chains on Akirin before and after immune challenge. S2 cells were transiently transfected with Akirin-V5 expressing plasmid. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-K63-polyUb coupled agarose beads. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-V5 antibodies. (C) Immunoprecipitation assay of Akirin after immune challenge. S2 cells were transiently transfected with Akirin-V5 expressing plasmid and dsRNA targeting GFP or Hyd. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 coupled agarose beads. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-K63-polyUb and anti-V5 antibodies. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation assay between over-expressed Akirin and Relish or Bap60 in S2 cells. The cells were transiently transfected with Akirin-V5 and Rel-HA or Bap60-HA expressing plasmids and dsRNA targeting GFP or Hyd. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 coupled agarose beads. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-HA or anti-V5 antibodies. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.