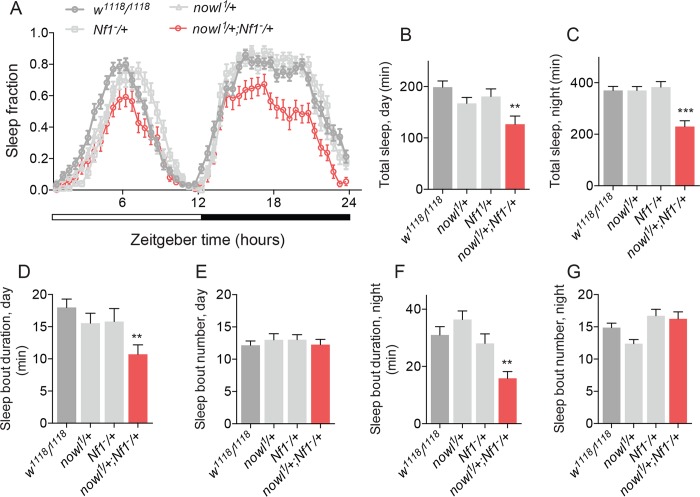
Fig 6. Interactions between nowl and Nf1 suggest that they act on a common sleep-regulatory mechanism.
(A) Sleep patterns of heterozygous nowl1/+ and Nf1-/+ females show that one copy of each is sufficient for maintaining proper sleep, while the trans-heterozygous (nowl1/+; Nf1-/+) mutants exhibit decreased sleep during both day and night. (B-G) Quantification of sleep parameters shows reduced average sleep-bout duration of trans-heterozygous nowl1/+; Nf1-/+ females, indicating that nowl and Nf1 interact to maintain sleep. Graphs represent means with SEM (n = 32) of data from one experiment. Significance was determined using Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post-hoc testing (*p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).