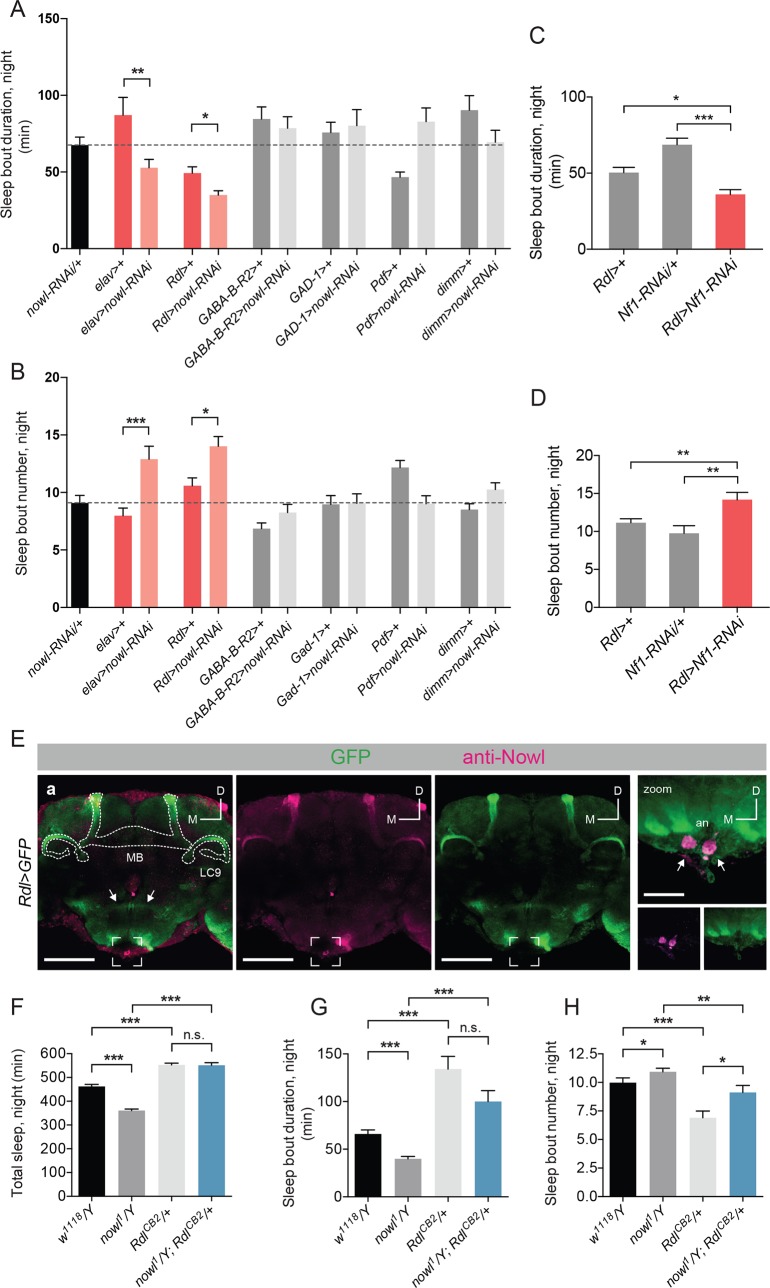
Fig 8. nowl is required in GABA-responsive neurons for sleep maintenance, and increased GABA signaling rescues the sleep phenotype of nowl mutants.
(A-D) Quantification of average male night-time sleep-bout duration and length. (A) Sleep-bout duration is decreased, and (B) sleep-bout number is increased during the night when nowl is knocked down pan-neuronally (elav>nowl-RNAi) or specifically in GABAA-receptor Rdl-expressing neurons (Rdl>nowl-RNAi) compared to controls (elav>+ and Rdl>+), respectively. Knockdown animals were compared to the GAL4 driver line crossed to w1118 (the genetic background for the RNAi), and elav>nowl-RNAi was used as a positive control. (C) Sleep-bout duration is decreased and (D) sleep-bout number increased in animals with knockdown of Nf1 in Rdl-expressing neurons compared to controls (Rdl>+ and Nf1-RNAi/+). (E) Anti-Nowl staining (purple) in males is prominent in Rdl-expressing neurons (Rdl>GFP, green) of the mushroom body (MB), among other sites. The neurons of the α′/β′ lobes of the MB (outlined; “MB”) and the neurons projecting to the LC9 optic glomerulus (outlined; “LC9”) express both Rdl>GFP and Nowl. Interneurons connecting the paired olfactory lobes (arrows) express Rdl>GFP but not Nowl, and a pair of neuronal clusters at the tip of the subesophageal ganglion (bracketed and zoomed in right panel) strongly express Nowl but not Rdl>GFP, indicating independent expression and staining. (F-H) Quantification of male night-time total sleep and average sleep-bout duration and number for w1118/Y, nowl1/Y, RdlCB2/+, and nowl1/Y; RdlCB2/+. (F) The reduced night-time sleep exhibited by nowl1 mutant flies is rescued by introducing one copy of the RdlCB2 allele. (G, H) Sleep-bout duration during the night is significantly decreased in nowl mutants, and sleep-bout number is significantly increased. Introducing one copy of the RdlCB2 allele partially rescues both defects. Graphs represent means with SEM (n = 32–156) of data pooled from one to five independent experiments. Significance was determined using Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's post-hoc testing (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001).