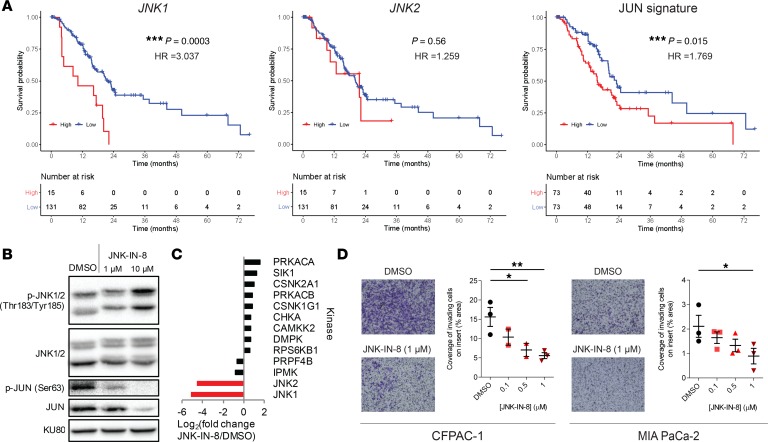
Figure 2. JNK-JUN inhibition with the highly specific irreversible inhibitor JNK-IN-8 is an attractive therapeutic strategy in PDAC.
(A) Kaplan-Meier plots comparing survival of patients with resected PDAC from the TCGA RNA-seq data set after splitting the cohort by expression of JNK1 or JNK2, or by the mean of rankings of 257 predicted JUN transcriptional targets (MSigDB: CREBP1CJUN_01). Significance determined by log-rank test shown with P values and hazard ratios (HR) determined by Cox proportional-hazards model. (B) Representative immunoblot after 12-hour treatment with DMSO or the covalent JNK inhibitor JNK-IN-8 in a P411-T1 PDX–derived cell line. KU80 used as loading control (n = 2). (C) MIB-MS analysis 1 hour after 1 μM JNK-IN-8 treatment in CFPAC-1 cells relative to DMSO-treated controls. JNK1 and JNK2 are highlighted in red. A total of 218 kinases were detected in both treatment and control; only kinases with |fold change| > 1.5 are shown. (D) Invasion through Matrigel transwells with representative images (original magnification ×20 [1 × 20]) and quantified growth analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (n = 2–3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.