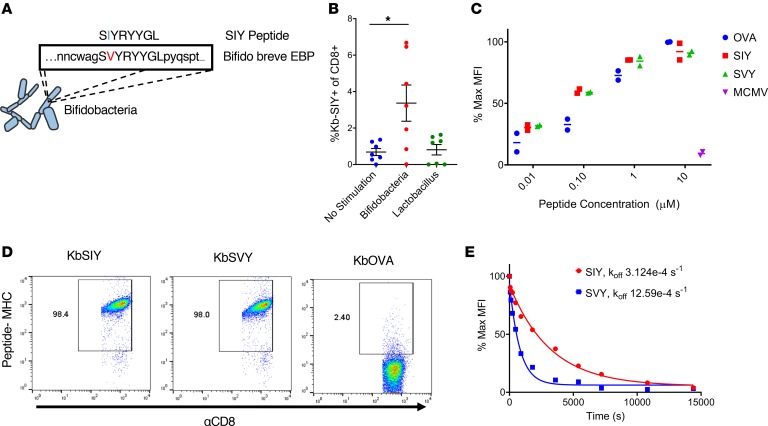
Figure 1. Commensal bacteria B. breve harbors the CD8+ T cell epitope SVY.
(A) Genetic map of B. breve, highlighting the homology of a peptide derived from B. breve exopolysaccharide biosynthesis protein (EBP) to the model epitope KbSIY. (B) Jackson mice splenocytes and mesenteric lymph node cells were cultured with or without heat-killed bacteria and tested for SIY-specific T cell expansion by staining with SIY peptide–loaded Kb-Ig dimer on day 11. Live CD8+ lymphocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry for KbSIY binding, with frequency determined by subtracting unloaded Kb-Ig staining frequency. P value = 0.011 by 1-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons. N = 7. Data represent mean ± SEM. (C) MHC stabilization assay: RMA-S cells were incubated overnight with peptide as indicated. Cell surface expression of H2-Kb was determined by flow cytometry. Reported values are relative to the H2-Kb mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) observed with 10 μM OVA peptide. mCMV, a non–Kb-restricted peptide, was used as a negative control. Data trended toward no difference between SIY and SVY groups. Data trended with no difference between SIY and SVY groups. N = 2. Data represent mean. (D) CD8+ T cells were isolated from the spleens of 2C TCR (SIY-reactive) transgenic mice and stained with 1 μg of cognate KbSIY-Ig, cross-reactive KbSVY-Ig, or irrelevant KbOVA-Ig. Representative data shown from 1 of 3 separate experiments. (E) Competitive off-rate binding assay of 2C CD8+ T cells with KbSIY or KbSVY peptide MHC dimer over time by the addition of 1B2 TCR-binding antibody. Cells were gated on CD8+. Cells were stained with KbOVA as a negative control or experimental pMHC to gate on antigen-specific cells over time. This competitive binding assay was performed twice, with similar koff rates determined each time.