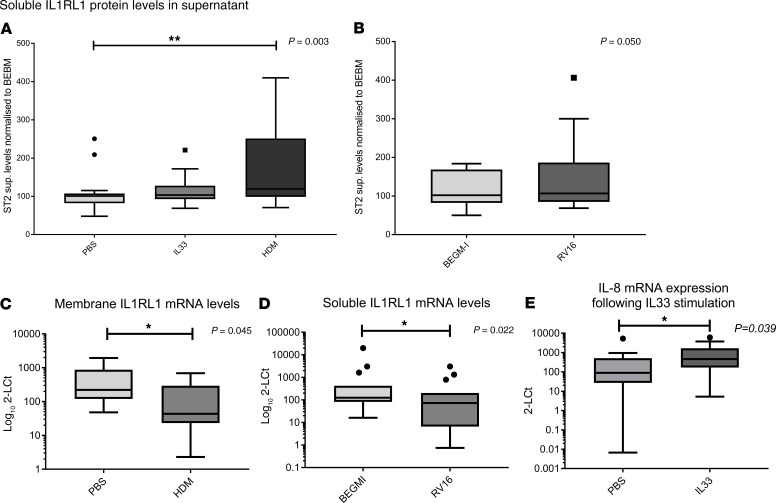
Figure 4. Asthma relevant microenvironments modulate IL1RL1 mRNA levels and soluble IL1RL1 protein levels in bronchial epithelial cells isolated from asthma patients and cultured in vitro.
(A) Stimulation of cells with 50 μg/mL house dust mite (HDM) for 24 hours resulted in increased release of soluble IL1RL1 into the cellular supernatant (P = 0.003, n = 18). (B) RV-16 (MOI: 1) stimulation for 24 hours did not significantly influence IL1RL1 protein release in the cell supernatants (P = 0.05, n = 18). (C and D) HDM stimulation resulted in a 3.5-fold reduction of membrane IL1RL1 mRNA (C) (P = 0.045, n = 15), while stimulation with RV-16 (MOI: 1) for 24 hours reduced soluble IL1RL1 mRNA levels 4.4-fold (D) (P = 0.022, n = 15). (E) IL-33 stimulation did not alter IL1RL1 protein or mRNA levels; however, it did induce IL-8 mRNA, demonstrating cell activation (P = 0.039, n = 18). Statistics were run using Mann-Whitney U test (B–E) or Kruskal-Wallis test (A), as relevant to the data. Data are represented by Tukey box and whisker plots, where the box covers data from the 25th to the 75th percentiles, with the center line denoting the median of the data. Whisker plots identify the interquartile range as determined by the Tukey method, with resulting outlier data displayed as distinct points outside the whiskers.