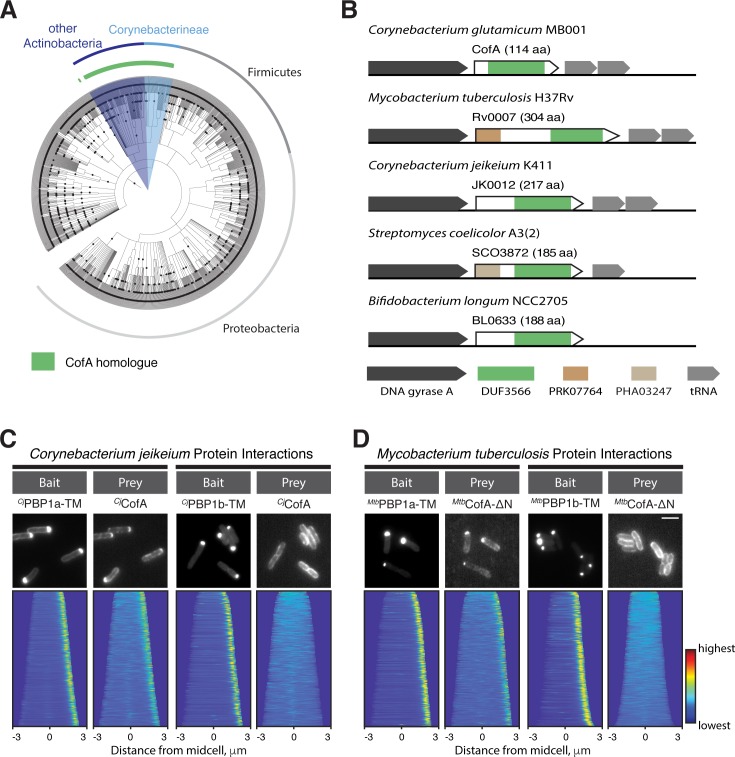
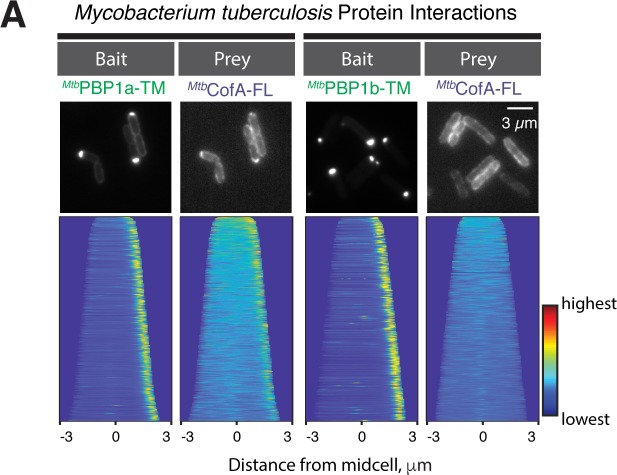
Figure 6. The CofA-PBP1a interaction is conserved.
(A) Phylogenetic tree showing the distribution of CofA-like proteins containing the DUF3566 domain. (B) Schematics showing the genomic organization of loci encoding cofA-like genes in representative bacteria. The domain predictions are based on the NCBI conserved domain database. Not drawn to scale. (C–D) POLAR two-hybrid assay assessing the interaction of CofA paralogs from Corynebacterium jeikeium K411 (C) or Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (D) with PBPs from these organisms. Results are displayed as in Figure 4. (C) (left) GFP fused to the transmembrane domain of C. jeikeium PBP1a (GFP-CjPBP1a-TM) with mScar-CjCofA prey. Reading frames used were JK1977 (residues 1–44) and JK0012, respectively. (right) GFP fused to the transmembrane domain of C. jeikeium PBP1b (GFP-CjPBP1b-TM) with mScar-CjCofA prey. Reading frames for PBP1b used was JK2069 (residue 185–235). Bar equals 3 µm. (D) POLAR two-hybrid assay results with Mtb proteins. (left) GFP fused to the transmembrane domain (residues 1–41) of Mtb PonA2 (GFP-MtbPonA2-TM) with mScar-MtbCofA-ΔN prey. Note PonA2 (Rv3682) is the Mtb ortholog of Cglu PBP1a. The CofA fusion used is deleted for the N-terminal extension (residues 1–190) found on the Mtb CofA sequence (Rv0007). (right) GFP fused to the transmembrane domain (residues 120–167) of Mtb PonA1 (GFP-MtbPonA1-TM) with mScar-MtbCofA-ΔN prey. Note PonA1 (Rv0050) is the Mtb ortholog of Cglu PBP1b. Bar equals 3 µm.