FIGURE 3.
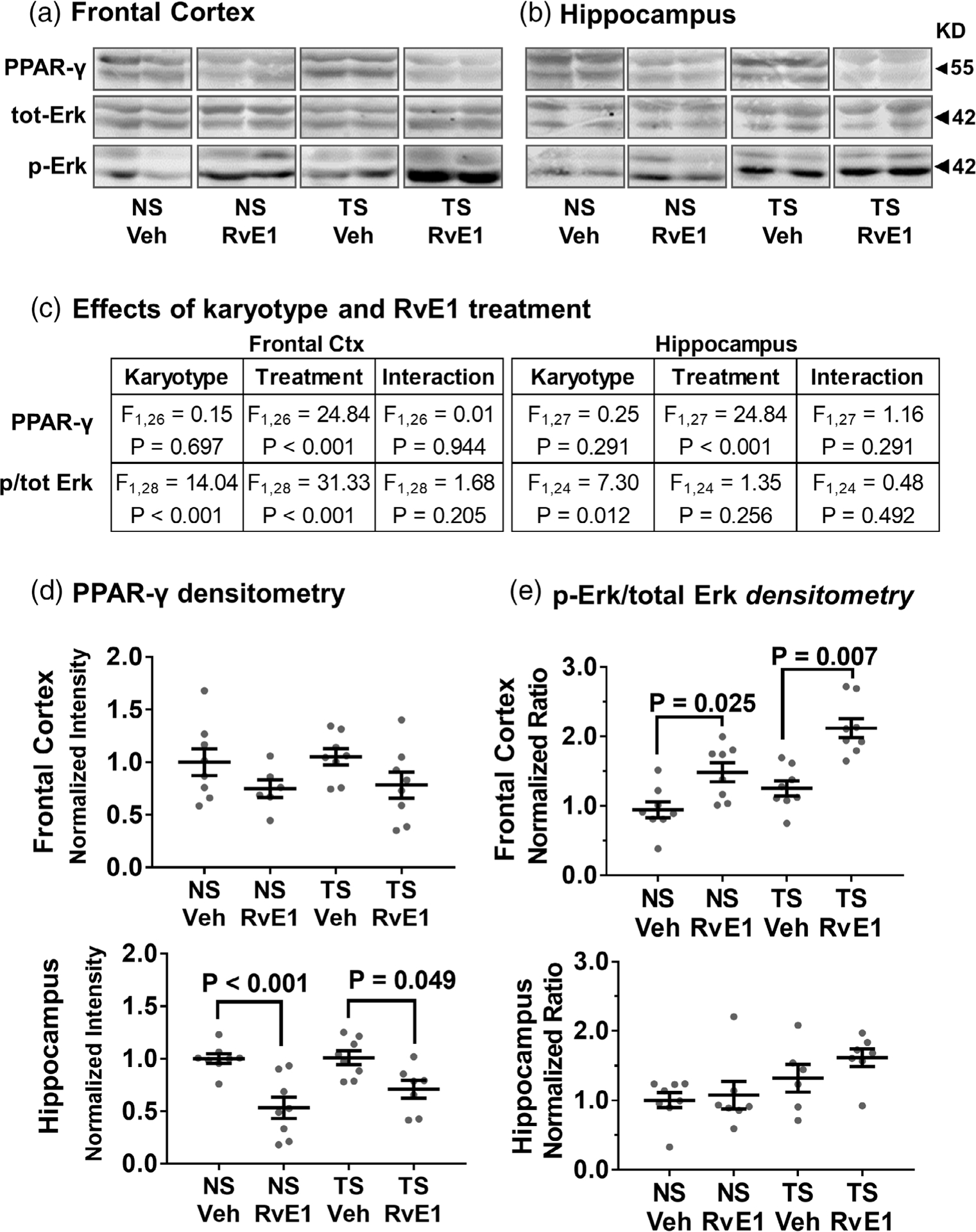
Effects of RvE1 on PPAR-γ levels and Erk1/2 phosphorylation. RvE1 treatment significantly reduced PPAR-γ levels and increased phosphorylated Erk1/2 immunoblot signals without significantly affecting total Erk1/2 levels in the frontal cortex (a) and hippocampus (b). (c) Two-way ANOVA effects by karyotype and RvE1 treatment on PPAR-y, ERK1/2 and phosphorylated (p) ERK1/2 were attributed mainly to RvE1 treatment for PPAR-γ and to treatment and karyotype for relative Erk signaling. (d,e) Densitometric analysis showed significant responses to RvE1-treatment in both NS and Ts65Dn mice for PPAR-γ (d) and relative Erk (e) signaling in frontal cortex and hippocampus. The lower band (Erk2) displayed a greater response compared to the upper band (Erk1). Tukey’s post hoc p values are shown for group comparisons. Relative Erk signaling reflects the ratio p-Erk over total Erk and error bars represent mean ± SEM. Erk1/2 = extracellular-signal-regulated kinase isoform 1 and 2; NS, normosomic; RvE1, resolvin E1; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; TS, Ts65Dn; Veh, vehicle
