FIGURE 5.
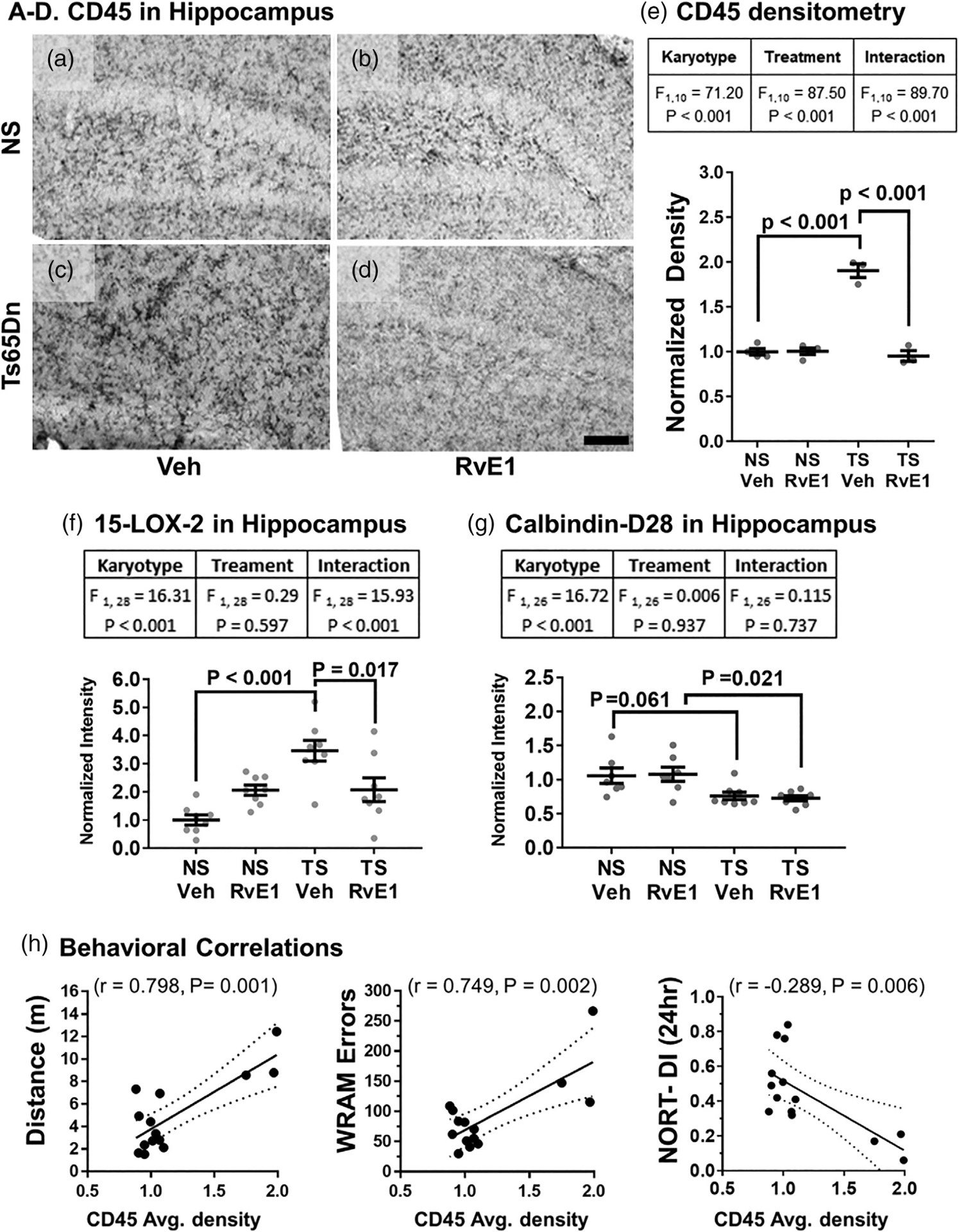
Microglial inflammatory response to RvE1 treatment. (a) Typical CD45-staining seen in Veh-treated NS mice showed multiple resting microglia with small cell somas and long, thin processes, which were not affected by RvE1 treatment (b). (c) Veh-treated Ts65Dn mice displayed elevated CD45-staining of microglial cells displaying an activated morphology compared to the NS mice (a). (d) RvE1 treatment reversed the microglial CD45 phenotype of Ts65Dn mice to staining patterns observed in NS cohorts. Scale bar equals 500 μm. (e) Two-way ANOVA effects by karyotype and RvE1 treatment for CD45 densitometry confirmed that RvE1 treatment significantly reduced CD45 staining density in Ts65Dn mice. (f) RvE1 treatment also reversed elevated 15-LOX-2 levels in the hippocampus of Ts65Dn mice. Two-way ANOVA effects by karyotype and RvE1 treatment of 15-LOX-2 densitometry confirmed that RvE1 treatment significantly reduced 15-LOX-2 levels in Ts65Dn mice. (g) Calbindin-D28 was significantly reduced in Ts65Dn mice and not affected by RvE1 treatment. Two-way ANOVA effects by karyotype only on averaged calbindin-D28 densitometry confirmed that RvE1 treatment had no effects on calbindin-D28 levels in Ts65Dn mice. Tukey’s post hoc p values are shown for group comparisons and error bars represent mean ± SEM. (h) CD45 density correlated significantly with spontaneous locomotion (positive correlation), total WRAM errors (positive correlation), and with NORT performance (negative correlation). Dotted lines represent 95% confidence interval. CD45, protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, C; 15-LOX-2, 15-Lipoxygenase-2; NS, normosomic; NORT-DI, novel object recognition discrimination index; RvE1, resolvin E1; TS, Ts65Dn; Veh, vehicle; WRAM, water radial arm maze task
