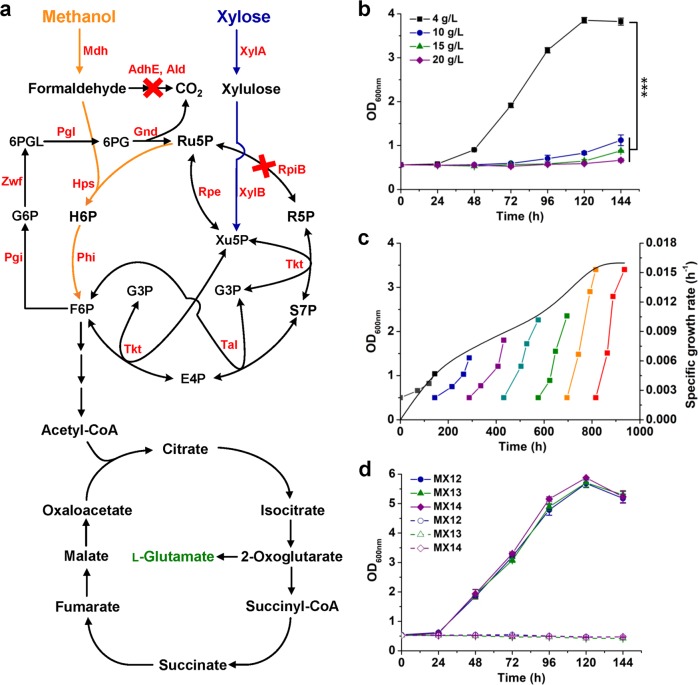
Fig. 1. Improving the tolerance to methanol via ALE.
a Detailed enzymatic reactions and metabolic pathways of the methanol-dependent C. glutamicum. Enzymes: methanol dehydrogenase (Mdh), 3-hexulose-6-phosphate synthase (Hps), 6-phospho-3-hexuloisomerase (Phi), mycothiol-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase (AdhE), acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (Ald), xylose isomerase (XylA), xylulokinase (XylB), ribose phosphate isomerase (RpiB), ribulose phosphate epimerase (Rpe), transketolase (Tkt), transaldolase (Tal), glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; (Pgi), glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase (Zwf), 6-phosphogluconolactonase (Pgl), 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (Gnd). Metabolites: ribose-5-phosphate (R5P), ribulose-5-phosphate (Ru5P), xylulose-5-phosphate (Xu5P), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), erythrose-4-phosphate (E4P), sedoheptulose-7-phosphate (S7P), fructose-6-phosphate (F6P), hexulose-6-phosphate (H6P), glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), 6-phospho-glucono-1,5-lactone (6PGL), and 6-phospho-gluconate (6PG). b Effects of methanol concentration on cell growth of methanol-dependent C. glutamicum MX-11. ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA, N = 3, P = 7.1 × 10−11. c ALE of strain MX-11 in CGXII minimal medium supplemented with 15 g/L methanol and 4 g/L xylose. The specific growth rate for each passage of ALE (the black curve) was calculated using the OD600nm values at the initial and final time points. d Growth curve of evolved methanol-dependent strains. Strains were cultivated using CGXII minimal medium supplemented with 15 g/L methanol and 4 g/L xylose (solid lines) or only xylose (dotted lines) as the carbon source(s). Values and error bars reflect the mean ± s.d. of three biological replicates (N = 3).