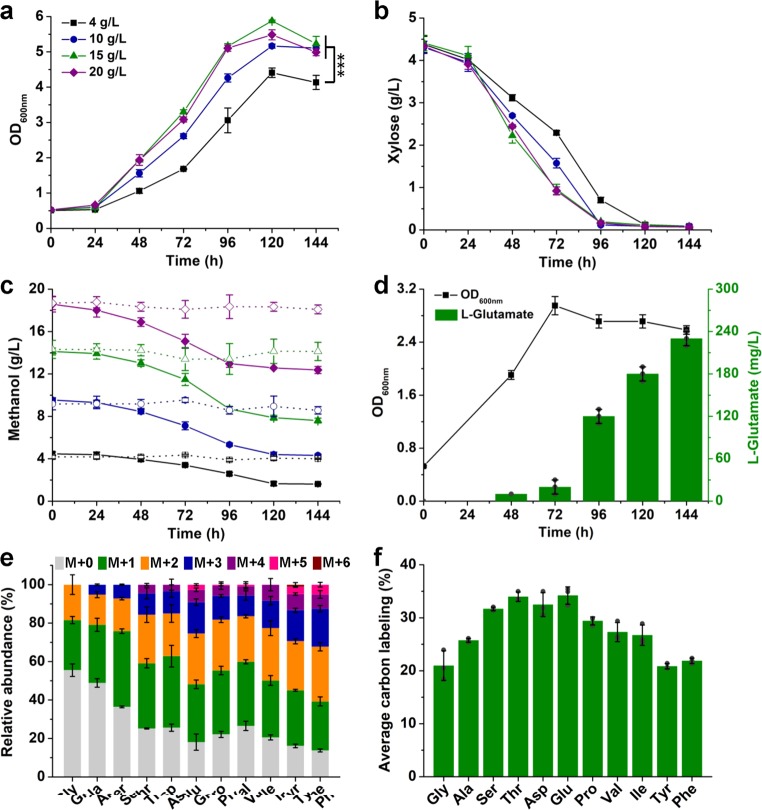
Fig. 2. Enhanced methanol bioconversion by evolved methanol-dependent C. glutamicum MX-14.
a–c Growth curve (a), xylose utilization (b), and methanol utilization (c) of strain MX-14 with different concentrations of methanol. Strain MX-14 was cultivated using CGXII minimal medium supplemented with 4, 10, 15, or 20 g/L methanol and 4 g/L xylose as the carbon sources. An evaporation control without inoculation of strain MX-14 was conducted simultaneously (dotted lines in c). ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA, N = 3, P = 1.2 × 10−4. d l-Glutamate production from methanol and xylose by strain MX-14. C. glutamicum MX-14 was cultivated in CGXII minimal medium supplemented with 15 g/L methanol and 4 g/L xylose. To induce l-glutamate production, penicillin G was added to a final concentration of 60 U/mL when the OD600nm of the culture reached ~3.0. e Relative abundance of proteinogenic amino acid mass isotopomers. f Average 13C-labeling of proteinogenic amino acids. C. glutamicum MX-14 was cultivated in CGXII minimal medium supplemented with 15 g/L 13C-methanol and 4 g/L non-labeled xylose. Cells were collected at 120 h for 13C-labeling analysis. Values and error bars reflect the mean ± s.d. of three biological replicates (N = 3).