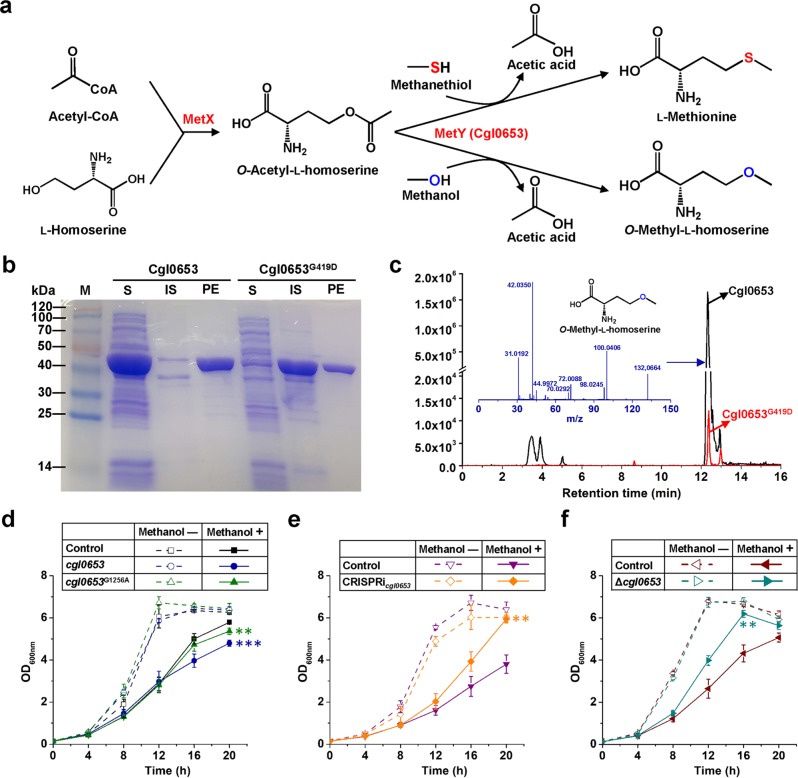
Fig. 5. Effects of cgl0653G1256A mutation (amino acid change of G419D) on enzyme activity and methanol tolerance.
a Cascade reaction for Cgl0653 activity assay and O-methyl-l-homoserine formation. l-Homoserine acetyltransferase (MetX), O-Acetyl-l-homoserine sulfhydrylase (MetY, Cgl0653). b Heterogeneous expression and purification of Cgl0653 and Cgl0653G419D. S Soluble supernatant of cell extract, IS insoluble sediment, PE purified enzyme. c LC-MS/MS analysis of O-methyl-l-homoserine after 20 min reaction. d Effects of cgl0653 and cgl0653G1256A overexpression on methanol tolerance. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA, N = 3; cgl0653, methanol + vs. control, methanol+, P = 3.0 × 10−4; cgl0653G1256A, methanol + vs. control, methanol+, P = 0.0070. e Effects of cgl0653 knock-down on methanol tolerance. **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA, N = 3; CRISPRicgl0653, methanol + vs. control, methanol+, P = 0.0015. f Effects of cgl0653 knock-out on methanol tolerance. **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA, N = 3; Δcgl0653, methanol + vs. control, methanol+, P = 0.0017. CGXII minimal medium supplemented with 5 g/L glucose and 30 g/L methanol was used to cultivate C. glutamicum ATCC 13032 and derivatives. IPTG (0.1 mM) was added at 4 h to induce cgl0653 or cgl0653G1256A overexpression and dCas9 expression. Values and error bars reflect the mean ± s.d. of three biological replicates (N = 3).