Figure 1.
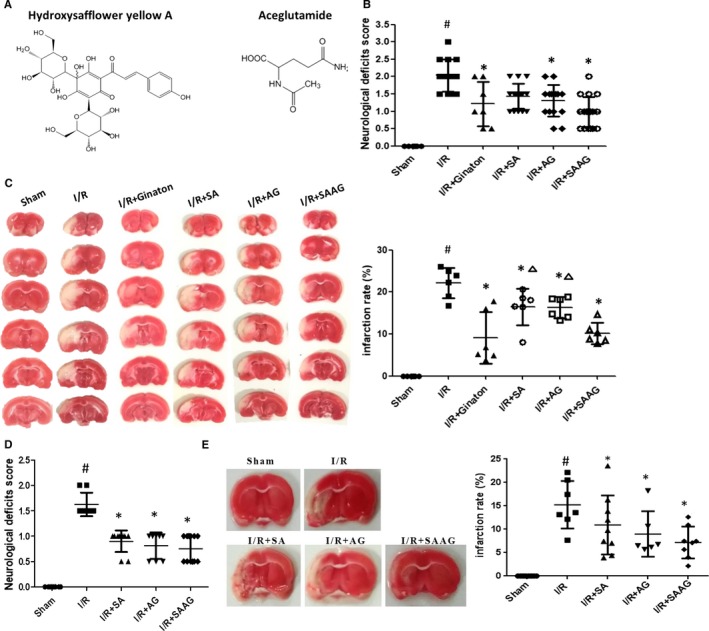
SAAG, SA and AG protected against cerebral I/R injury at day 2 and day 12. A, The chemical structures of hydroxysafflower yellow A (the main ingredient of SA) and AG; B, Neurological deficient scores at day 2 (n = 7 for I/R + Ginaton and n = 14‐18 for other groups); C, Representative TTC staining images with the quantified infarction ratio using imageJ at day 2 (n = 6); D, Neurological deficient scores at day 12 (n = 8‐12); E, Representative TTC staining images with the quantified infarction rate using imageJ at day 12 (n = 6‐8); According to the instruction of SAAG, every millilitre of SAAG contained 30 mg AG and 0.5 g SA, thus 1.25 g/kg of SA and 75 mg/kg of AG were also evaluate to investigate the role of each composition of SAAG on the protection against cerebral I/R injury, respectively. # P < .05 compared with the sham group, *P < .05 compared with the I/R group, and ∆ P < .05 compared with the I/R + SAAG group
