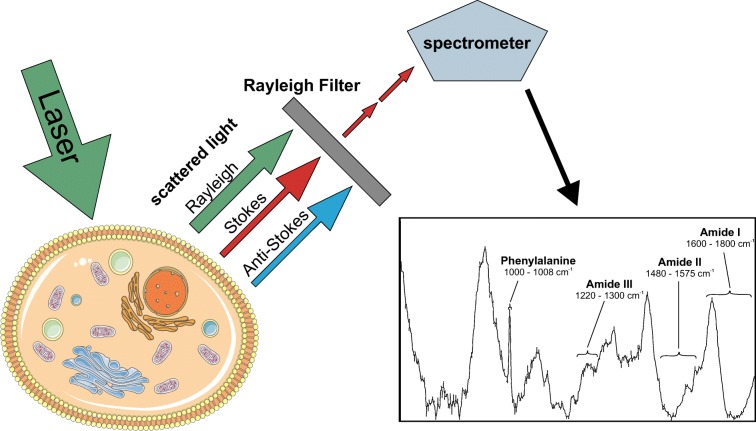
Fig. 1.
Raman microspectroscopy of cells. Photons emitted from a laser light source are differentially scattered by chemical bonds of cellular constituents. Rayleigh and anti-Stokes scattered light is filtered, and remaining Raman Stokes scattered photons are recorded by the spectrometer. A typical Raman spectrum of mammalian cells is shown. Spectral regions explaining the most prominent differences between cellular states are depicted