Fig. 8.
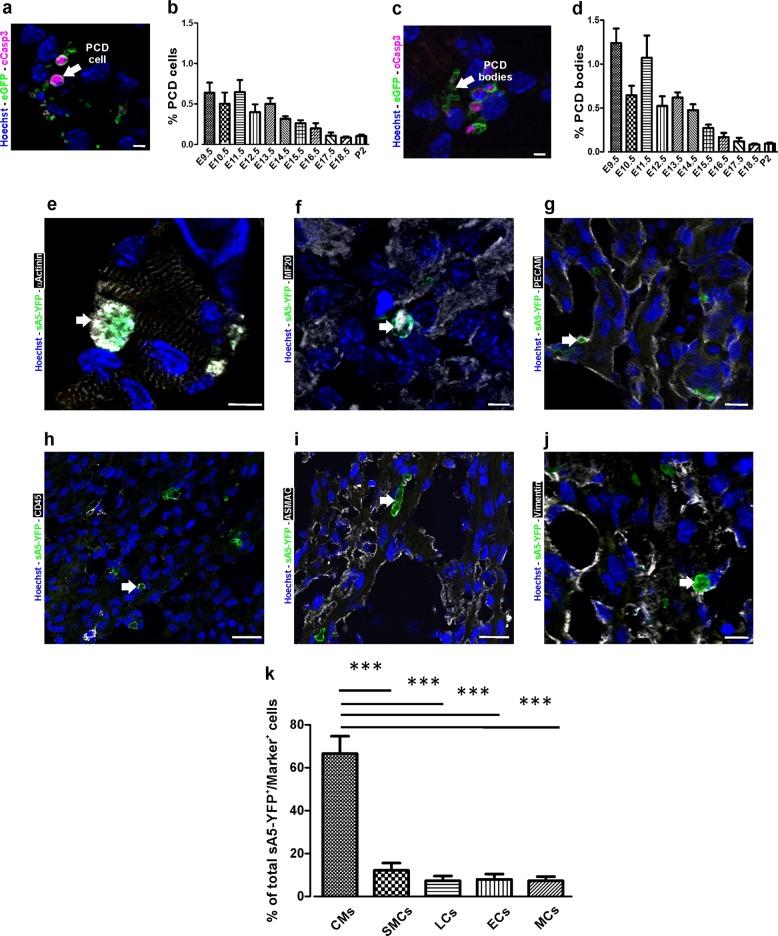
Identification and quantitation of the different cell types undergoing PCD during heart development. a Sagittal section of a transgenic heart at E12.5 depicting PCD cells. PCD cells were defined by condensed nuclei, a clear ring-like membrane sA5-YFP accumulation, and/or cCasp3+ signal. b Quantitation of PCD cells (white arrow in a). c Sagittal section of a transgenic heart at E12.5 depicting bodies of PCD cells. PCD Bodies were defined as smaller particles (2–4 µm) without nuclear signal and positive for either sA5-YFP or cCasp3 or both. d Quantitation of PCD bodies (white arrow in c). e–j Co-stainings in sections of transgenic embryonic hearts (E13.5) stained for cardiomyocyte (CMs, α-actinin, and MF20), endothelial cell (ECs, PECAM), leukocyte (LCs, CD45), smooth muscle cell (SMCs, ASMAC), and mesenchymal cell (MCs, vimentin) markers. k Quantitation of the different cell types that undergo PCD during heart development. Hoechst nuclear staining and sA5-YFP secreted human Annexin V-yellow fluorescent protein. Bars are 5 µm (a, c, e, f), 10 µm (g, j), and 20 µm (h, i). Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m.,***P < 0.001 ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test; n = 7–13