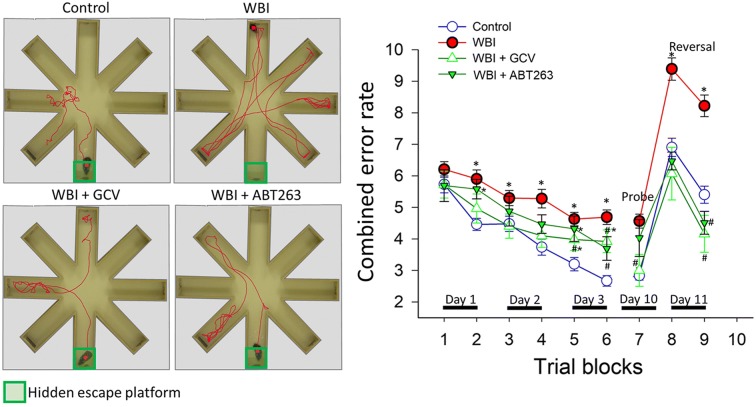
Fig. 7.
Rescue of NVC responses by elimination of senescent cells improves performance of WBI-treated p16-3MR mice in the radial-arm water maze (RAWM). Control p16-3MR mice and WBI-treated p16-3MR mice that received vehicle, ganciclovir (GCV), or ABT263 were tested in the RAWM. a Representative probe test search path of a randomly selected animal from each group is shown with the target position highlighted in green. Note the WBI-treated mice that received vehicle required more time and a longer path length in order to find the hidden escape platform than both control animals and GCV- or ABT263-treated WBI mice. This particular WBI-treated mouse did not even find the platform within the allowed time. The WBI-treated mouse also re-entered a previously visited arm multiple times. b WBI-treated animals have higher combined error rates throughout day 2 and 3 of the learning phase, and the retrieval day 10 as compared with control animals. WBI-treated animals also make significantly more errors during probe reversal than control animals. In contrast, WBI-treated mice treated with GCV or ABT263 perform this task significantly better than untreated irradiated mice. Combined error rate is calculated by adding 1 error for each incorrect arm entry as well as for every 15 s spent not exploring the arms. All data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 20 for each data point). *P < 0.05 vs. control, #P < 0.05 vs. vehicle treated WBI