Fig. 1.
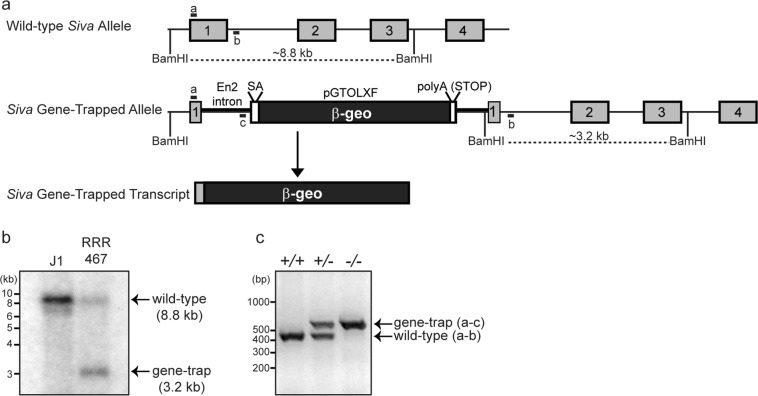
Generation of Siva-knockout mice. a Schematic representation of Siva gene-trapped allele and transcript. The gene trap vector consists of Engrailed 2 (En2) intronic sequences followed by a splice acceptor (SA) and coding sequences for the β-galactosidase-neomycin (β-geo) gene. An SV40 polyA sequence acts as a transcriptional stop element. The gene-trapped transcript consists of the Siva 5’UTR and sequences encoding the first 3 amino acids from Siva exon1 fused to β-geo. BamHI sites and PCR primers used for genotyping are indicated. b Southern blot analysis of J1 (WT) and RRR467 (Siva gene trap) ES cell DNA demonstrates disruption of the Siva locus in the gene-trapped ES cells. Following DNA digestion with BamHI, Siva exon 2 sequences were used as a probe. (c) Genotyping PCR used to identify Siva+/+, Siva+/−, and Siva−/− mice and embryos. The forward primer recognizes a portion of 5′-UTR from Siva exon 1 (primer “a”) and is used in combination with reverse primers to a region of intron 1 (primer “b”) and the gene trap vector (primer “c”) The expected band sizes for the wild-type and gene-trapped alleles are 415 and 550 bp, respectively