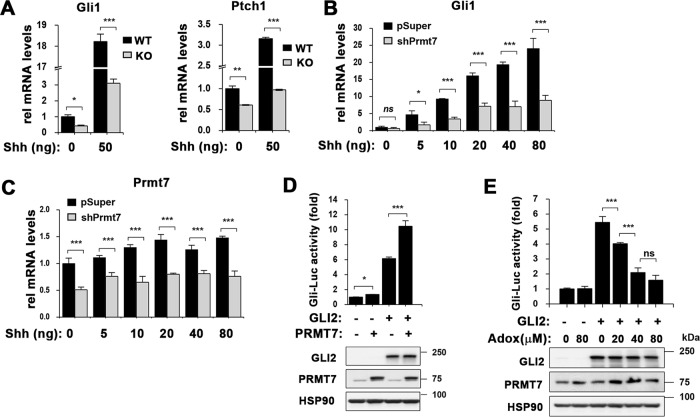
Fig. 2.
PRMT7 deficiency blunts Shh signaling activity. a qRT-PCR analysis for Shh signaling components, Gli1 and Ptch1. PRMT7+/+ (WT) and PRMT7−/− (KO) MEFs were treated with 50 ng/ml recombinant Shh for 12 h. Data are presented as means ± SD. n = 3, ns = not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. b qRT-PCR analysis for Gli1 mRNA expression in control shRNA-expressing or PRMT7 shRNA-expressing 10T1/2 cells treated with increasing amounts of Shh for 12 h. ns = not significant, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 for the comparison to control by ANOVA test. n = 3. c qRT-PCR analysis for PRMT7 mRNA expression with the total RNAs shown in panel b. Data are presented as means ± SD. n = 3, ***P < 0.001. d GLI2-responsive luciferase activities in 10T1/2 cells transfected with indicated expression vectors (upper panel). The protein expressions of GLI2 and PRMT7 were determined by western blot (lower panel). Data are presented means ± SD. n = 3, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. e The effect of arginine methylation inhibition on GLI-reporter activities. Control-expressing or GLI2-expressing 10T1/2 cells were treated with control vehicle or a PRMT inhibitor, Adox with increasing concentration for 24 h (upper panel). The protein expressions of GLI2 and PRMT7 were determined by western blot (lower panel). Data are presented means ± SD. n = 3, ns = not significant, ***P < 0.001