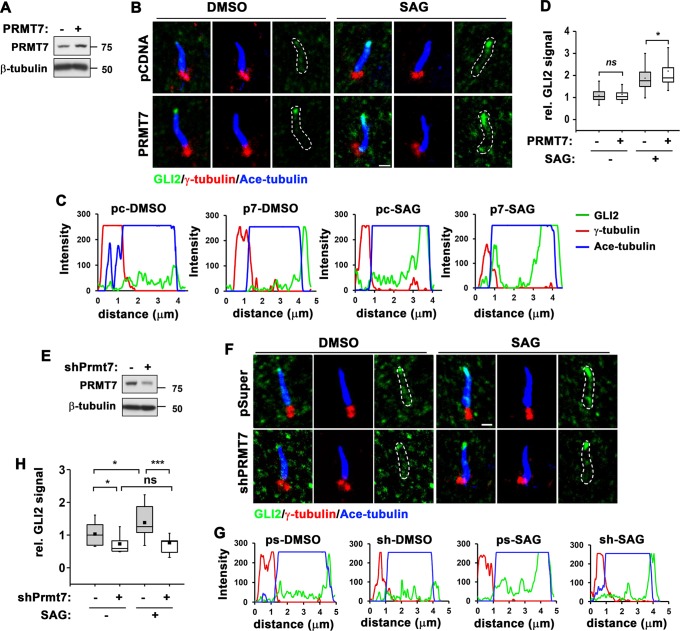
Fig. 3.
PRMT7 inhibition reduces ciliary localization of GLI2 in response to SAG. a Immunoblot for PRMT7 expression in 10T1/2 cells transfected with control or PRMT7 expression vector. b Immunostaining for GLI2, acetylated-tubulin (a marker for primary cilium, Ace-tubulin) and γ-tubulin (a marker for the basal body of the primary cilium) in control or PRMT7 overexpressing cells treated with vehicle or SAG for 12 h. Scale bar: 1 μm. c The signal intensity of GLI2 from the base to the tip of primary cilium shown in panel b was quantified. d The relative signal intensity of GLI2 in primary cilium shown in panel b was indicated. The value from the vehicle-treated control cells was set to 1.0. Data are presented as means ± SD. n ≥ 15. ns; not significant. *P < 0.05. e Immunoblot for PRMT7 in 10T1/2 cells expressing control or PRMT7 shRNA. f Immunostaining for GLI2, Ace-tubulin and γ-tubulin in control or PRMT7-depleted cells treated with vehicle or SAG for 16 h. Scale bar: 1 μm. g The signal intensity of GLI2 from the base to the tip of primary cilium shown in panel f was quantified. h The relative signal intensity of GLI2 in primary cilium shown in panel f was indicated. The value from the vehicle-treated control cells was set to 1.0. Data are presented as means ± SD. n ≥ 15. ns = not significant. *P < 0.05. ***P < 0.001