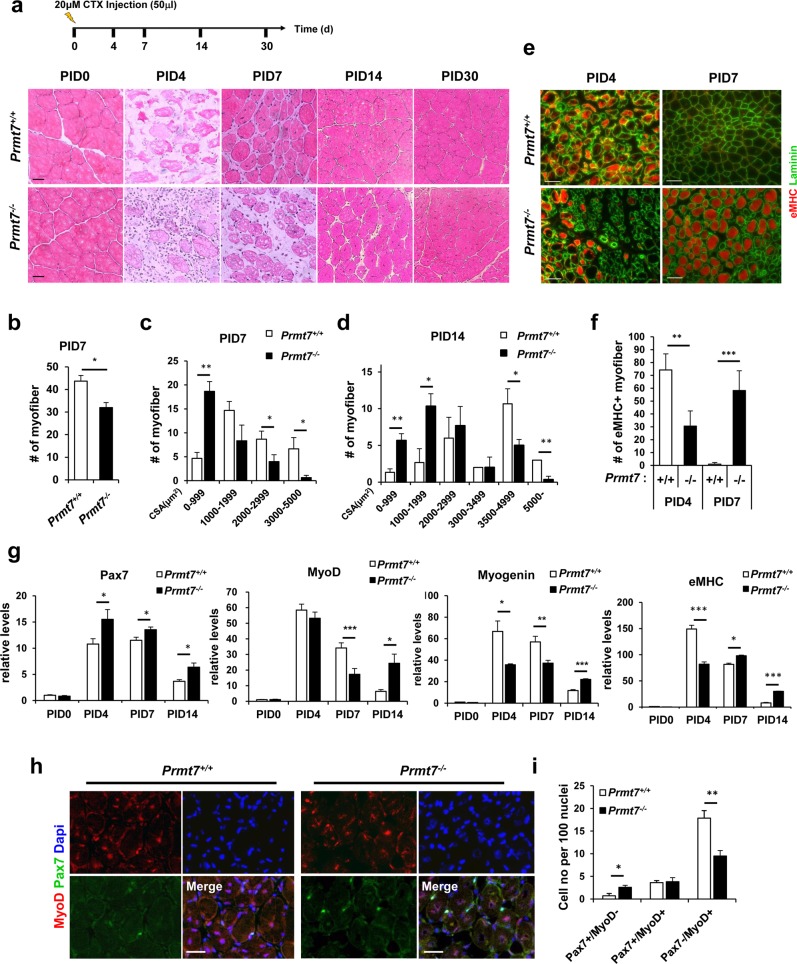
Fig. 2.
Mice Lacking Prmt7 Exhibit Delayed Muscle Regeneration. a The scheme of cardiotoxin injury and representative images of hematoxylin and eosin stained sections of TA muscles from Prmt7+/+ and Prmt7−/− mice harvested at 0, 4, 7, 14 and 30 days post cardiotoxin injury (PID). Scale bar, 20μm. b Quantification of the number of eosin-positive myofibers from Prmt7+/+ and Prmt7−/− TA muscles at 7 days after injury. c, d Quantification of the cross-sectional area of Prmt7+/+ and Prmt7−/− TA muscles at 7 and 14 days following injury. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 3 mice per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. e Immunostaining of TA muscles from Prmt7+/+ and Prmt7−/− mice with anti- eMHC and anti-laminin antibodies at 4 and 7 days post injury. f Quantification of the number of eMHC-positive myofibers. Values are means ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (n = 3). g Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for various myogenic markers in Prmt7+/+ and Prmt7−/− TA muscles at indicated time points (post injury days 0, 4, 7 and 14) after CTX injury. Markers analyzed are Pax7, MyoD, Myogenin and eMHC. Values are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (n = 3). h Immunostaining of TA muscles from Prmt7+/+ and Prmt7−/− mice at 7 days after CTX injury with anti-Pax7 and anti-MyoD antibodies. i Quantification of the number of cells undergoing self-renewal (Pax7+/MyoD-), activation (Pax7+/MyoD+) and differentiation (Pax7-/MyoD+). Values are means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (n = 3)