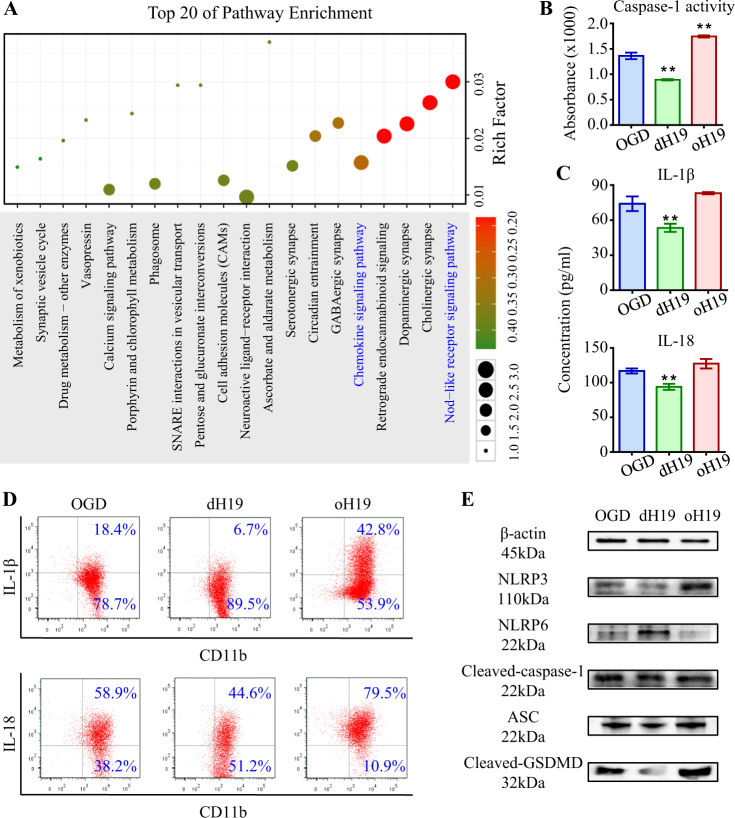
Fig. 2.
H19 regulates neuro-inflammation by rebalancing NLRP3/NLRP6 inflammasomes. a GO analysis annotated biological function to dysregulated mRNAs in I/R retina. Canonical pathways related to Nod-like receptor signaling and chemokine production acquired vital importance in I/R injury. b In primary microglia, H19 knockout significantly prevented OGD/R-induced caspase-1 activation, which was exacerbated by H19 overexpression. c As measured by ELISA, OGD/R-induced overproduction of IL-1β and IL-18 was suppressed by H19 knockout and aggravated by H19 overexpression in cultured microglia. d As measured by flow cytometry, H19 excision effectively decreased IL-1β or IL-18 overproduction in microglia. And H19 overexpression increased production of these two pro-inflammatory cytokines. e Reciprocal activation of NLRP3/NLRP6 inflammasomes was observed in microglia underwent OGD/R. Imbalance activation of inflammasomes resulted in increased ASC and cleavage of caspase-1 and GSDMD. The upregulation of these pro-inflammatory proteins was aggravated in oH19 microglia as attenuated by H19 knockout as measured by immunoblot. The relative level of each target protein was normalized to β-actin from the same sample (Fig. S2H). Data were represented as means ± SD (n = 6). Compared with the OGD/R group (OGD): **P < 0.01. OGD/R, oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion; dH19, H19 knockout; oH19, H19 overexpression; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD