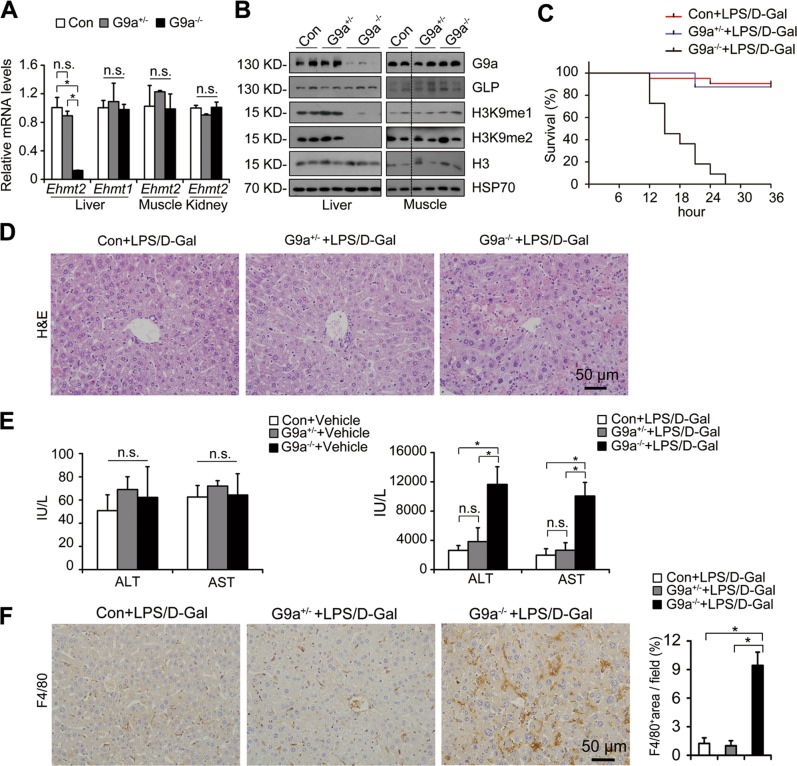
Fig. 1.
Hepatic G9a deletion aggravates LPS-induced liver damage. a Relative mRNA levels of Ehmt2 and Ehmt1 in the liver, muscle and kidney of Control, L-G9a+/− and L-G9a−/− mice. b Representative western blots for G9a, GLP, H3K9me1, H3K9me2, H3, and HSP70 in the liver and muscle of Control, L-G9a+/− and L-G9a−/− mice. c Survival rate (n = 21 for Controls; n = 16 for L-G9a+/− mice; n = 11 for L-G9a−/− mice) and d H&E staining (n = 6–8 per group; scale bar, 50 μm) after LPS/d-Gal co-injection. e Serum levels of ALT and AST with or without LPS/d-Gal co-injection. f Representative pictures for F4/80 staining in livers (left) and quantitative results (right) after LPS/d-Gal co-injection (scale bar, 50 μm). All data were obtained from male mice. n = 3–4 per group; n.s., not significant; *p < 0.05