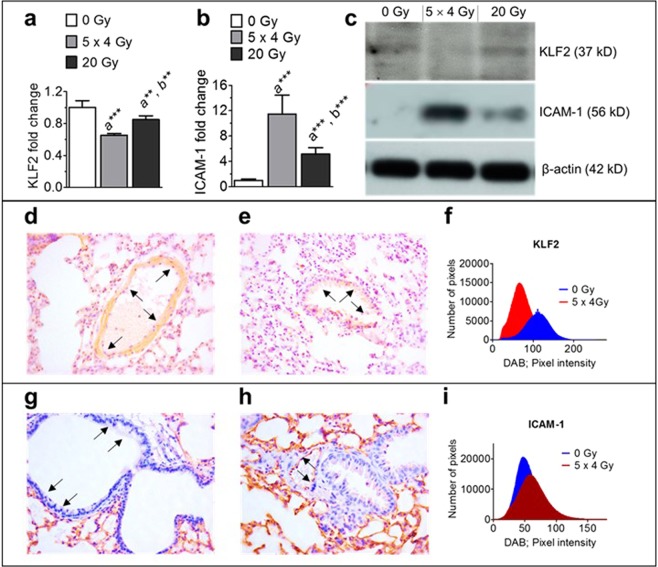
Figure 6.
Fractionated thoracic irradiation suppressed KLF2 and enhanced ICAM-1 levels in the lung. Quantification of KLF2 (a) and ICAM-1 (b) protein levels and representative Western blot analysis (c) in the lung tissue of mice (n = 6) at 24 h following 5 fractions of 4 Gy at 24 h intervals or single exposure to 20 Gy. β-actin served as a loading control. KLF2 immunostaining in the lung tissue samples of sham irradiated (d), irradiated (e), and quantitation (f) at 24 h after exposure to 5 fractions of 4 Gy at 24 h intervals or single exposure to 20 Gy. ICAM-1 immunostaining in the lung tissue samples of sham irradiated (g), or irradiated (h), and quantitation (i) at 24 h after exposure to 5 fractions of 4 Gy at 24 h intervals or single exposure to 20 Gy. (n, number of independent experiments performed; a, significant statistical difference between nonirradiated and irradiated groups; b, significant statistical difference between fractionated irradiation and single exposure; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).