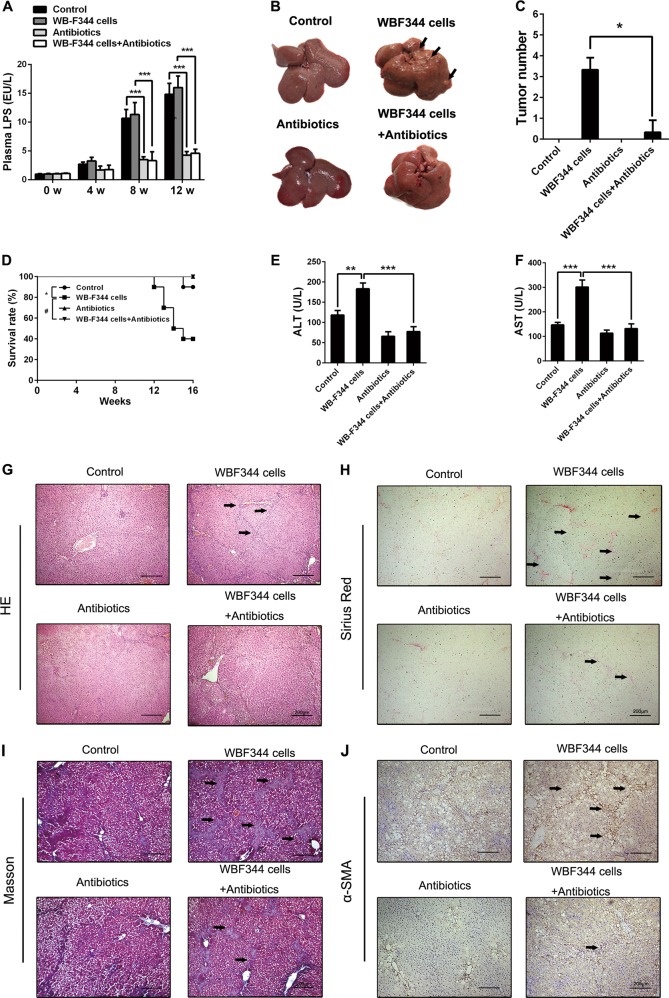
Fig. 4.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) elimination alleviated hepatic progenitor cell (HPC) transplantation-induced hepatocarcinogenesis and liver fibrosis in primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) model. a A combination of four different antibiotics, including ampicillin (1 g/l; Sigma), neomycin sulfate (1 g/l; Sigma), metronidazole (1 g/l; Sigma), and vancomycin (500 mg/l; Abbott Labs) was used to eliminate gut-derived LPS during HCC occurence. Serum LPS levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the indicated groups. Data are represented as mean ± SD. ***p < 0.001. b, c Rat livers of the indicated groups. The number of HCC nodules per liver in rats was determined at the eighth week after diethylnitrosamine (DEN) treatment. Data are represented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05. d Survival rate was observed. LPS elimination alleviated the death in DEN-treated rats. Data are represented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 and #p < 0.01. e, f Serum levels of AST and ALT were determined to indicate the extent of liver damage. Data are represented as mean ± SD. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. g Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was employed to observe the histological structure in different groups. h–j Hepatic collagen deposition was determined by Sirius Red staining and Masson’s trichrome staining. Expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) was detected by immunohistochemical analysis