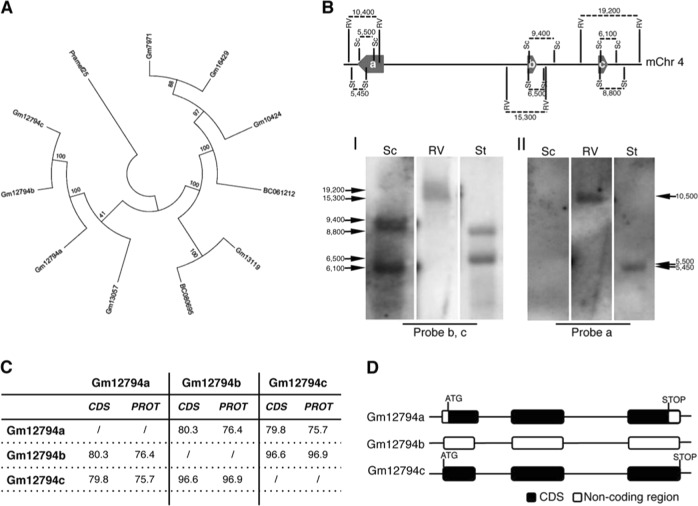
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of RA-induced Prame genes and characterization of Gm12794c genetic locus. a A maximum parsimony tree reflecting similarities among the RA-induced murine Prame genes has been generated using MEGA7. The tree is based on the bootstrap method for phylogenetic testing with a number of bootstrap replications equal to 1000. The Subtree–Pruning–Regrafting (SPR) validated the tree topology. Numbers indicate phylogenetic distance. b (Up) A schematic representation of the Gm12794 genetic locus on murine chromosome 4 is shown. Relative positions of EcoRV (RV), SacI (Sc) and StuI (St) DNA sites, and digestion fragments lengths are indicated. Thick arrows labeled as a, b, and c represent Gm12794a, Gm12794b, and Gm12794c genes, respectively. (Down) mESCs genomic DNA has been digested with the indicated restriction enzymes and probed with probes b and c to identify Gm12794b and Gm12794c gene loci (I) and probe a to validate Gm12794a locus (II). Arrows indicated the expected fragments. c Similarities among coding sequences (CDS) and putative protein sequences of Gm12794a, Gm12794b, and Gm12794c genes are shown as percentage. d Schematic representation of coding and non-coding sequences of Gm12794a, Gm12794b and Gm12794c genes