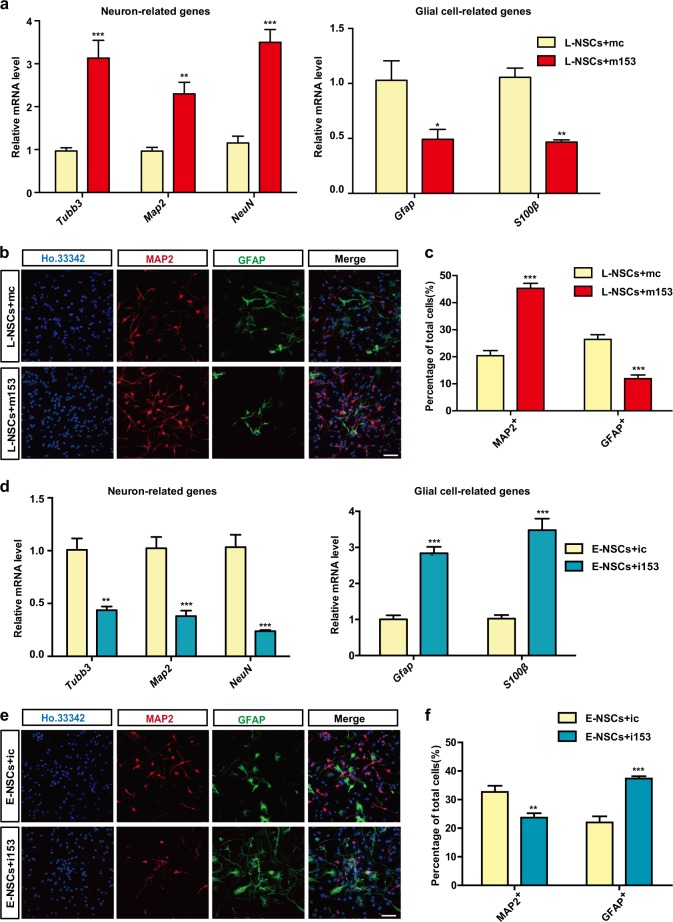
Fig. 2.
miR-153 promotes neurogenesis and inhibits gliogenesis. a Quantitative RT-PCR detection of neuron-related genes (Tubb3, Map2, NeuN) and astrocyte-related genes (Gfap, S100β) in the neural differentiation of L-NSCs + mc or L-NSCs + m153 (L-NSCs transfected with control or miR-153 mimics). b Immunofluorescence analysis of neural differentiation with L-NSCs + mc or L-NSCs + m153 as evaluated by MAP2 (red), GFAP (green), and Ho.33342 (blue). Scale bar: 50 μm. c Percentages of MAP2-positive and GFAP-positive cells in differentiation. d Quantitative RT-PCR detection of neuron-related genes and glial cell-related genes in the neural differentiation of E-NSCs + ic or E-NSCs + i153 (E-NSCs transfected with ctrl or miR-153 inhibitor). e Immunofluorescence analysis of neural differentiation with E-NSCs + ic or E-NSCs + i153 as evaluated by MAP2 (red), GFAP (green), and Ho.33342 (blue). Scale bar: 50 μm. f Percentages of MAP2-positive and GFAP-positive cells in neural differentiation. Data information: the data shown are the mean ± SEM, n = 3; ANOVA; ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. Gapdh was used as an internal control for normalization in quantitative RT-PCR. L-NSCs late NSCs, E-NSCs early NSCs, mc control mimics, m153 miR-153 mimics, ic control inhibitor, i153 miR-153 inhibitor