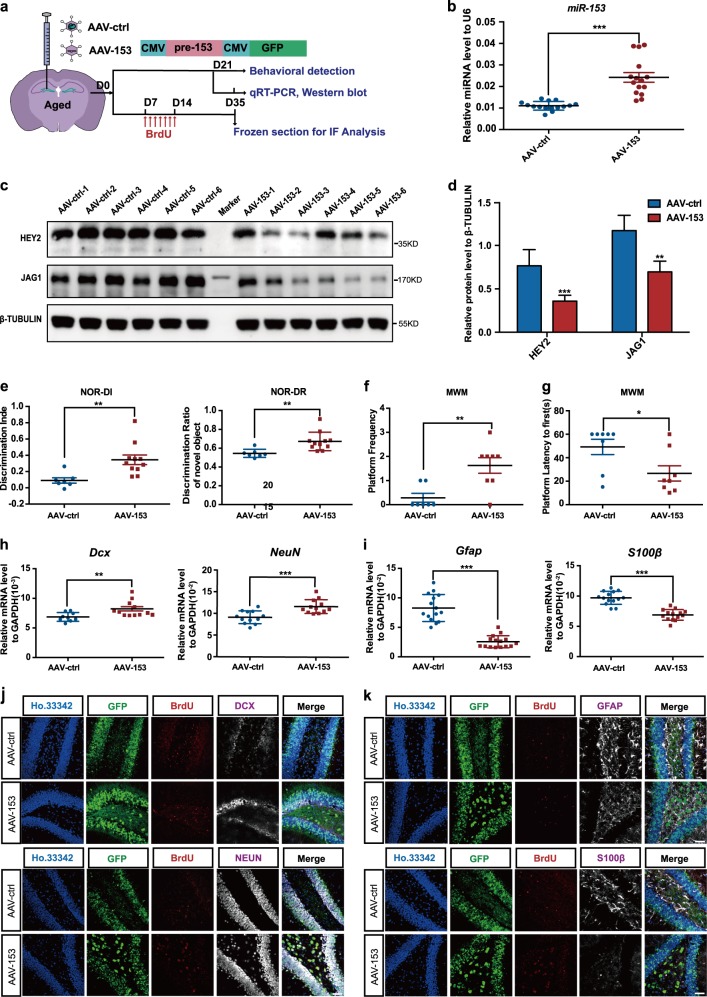
Fig. 7.
miR-153 increases adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus and enhances the cognitive abilities of aged mice. a Schematic of virus injection into the hippocampi of aged mice and diagram of the detection process. b Quantitative RT-PCR detection of miR-153 in the hippocampi of AAV-ctrl and AAV-153 aged mice; AAV-ctrl, n = 15; AAV-153, n = 15. c Western blot analysis of the protein levels of JAG1 and HEY2 in the hippocampi of AAV-ctrl and AAV-153 aged mice normalized to β-TUBULIN. d Statistical analysis of the grayscale levels of JAG1 and HEY2 by ImageJ; AAV-ctrl, n = 6; AAV-153, n = 6. e Discrimination index and discrimination ratio of novel objects; AAV-ctrl, n = 7; AAV-153, n = 11. f, g Platform crossings and amounts of time required for the mice to first reach the platform area during the water maze test; AAV-ctrl, n = 7; AAV-153, n = 8. h, i Quantitative RT-PCR detection of the newborn neuronal marker Dcx (AAV-ctrl, n = 9; AAV-153, n = 12), the mature neuronal marker NeuN (AAV-ctrl, n = 12; AAV-153, n = 12), and the glial cell markers Gfap (AAV-ctrl, n = 15; AAV-153, n = 15) and S100β (AAV-ctrl, n = 14; AAV-153, n = 14) in the hippocampi of AAV-ctrl and AAV-153 aged mice. j Immunofluorescence analysis of neurons in the hippocampi of AAV-ctrl and AAV-153 aged mice as evaluated by GFP (green), BrdU (red), DCX (white), NEUN (white), and Ho.33342 (blue). Scale bar: 50 μm. k Immunofluorescence analysis of astrocytes in the hippocampi of AAV-ctrl and AAV-153 mice as evaluated by GFP (green), BrdU (red), GFAP (white), S100β (white), and Ho.33342 (blue). Scale bar: 50 μm. Data information: the data shown are the mean ± SEM; Student’s t test; ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. aged mice 16–18 months old, NOR novel object recognition, MWM Morris water maze