Fig. 1.
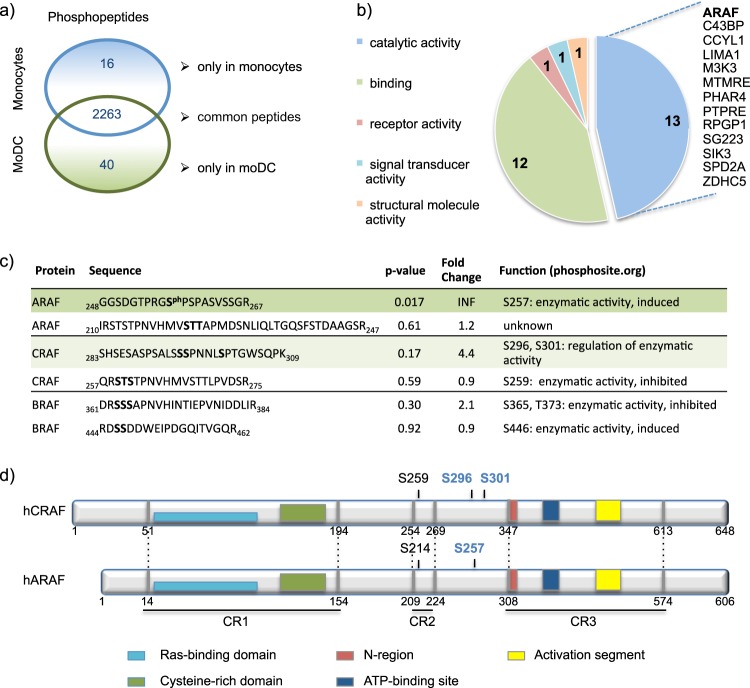
Phosphoproteome analysis of monocytes and moDCs. a Mass spectrometry-based proteome analysis was performed to compare the phosphoproteome of human monocytes with moDCs. Monocytes were isolated from buffy coats and cultured for 24 h in X-VIVO-15 medium supplemented with 1% heat-inactivated plasma. MoDCs were obtained through culturing monocytes with GM-CSF/IL-4 for 5 days. The Venn diagram shows phosphopeptides attributed to monocytes or moDCs detected in all three biological replicates of the respective samples. b The corresponding proteins of the phosphopeptides, detected exclusively in moDCs, were classified using Panther Classification System with the settings “GO:Slim Molecular Function” covering 28 proteins including ARAF. c Phosphopeptides of ARAF, BRAF, and CRAF are presented, which were identified in all three replicates of either monocytes or moDCs. Potential phosphorylation sites of the phosphorylated peptides are shown in bold. Among the identified phosphopeptides, the ARAF phosphopeptide covering amino acids 248–267 was the only one being significantly upregulated in moDCs. The CRAF phosphopeptide covering amino acids 283–309, which was found to be mono- and diphosphorylated, was higher in moDCs, but not significantly enriched. d The ARAF and CRAF phosphopeptides described in c, are located between the conserved regions CR2 and CR3