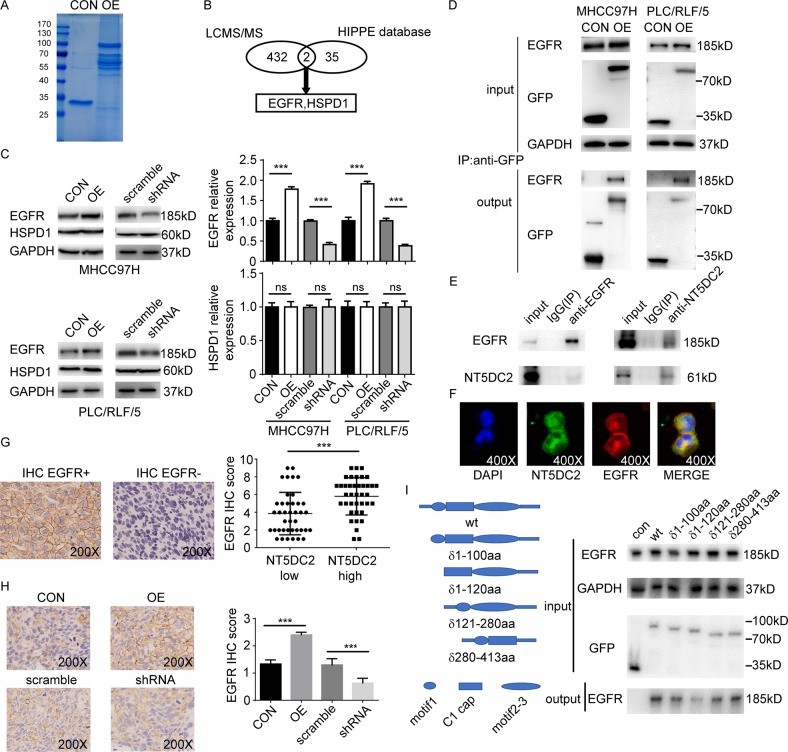
Fig. 4. NT5DC2 binds to EGFR and regulates EGFR expression.
a Coomassie blue staining of anti-GFP coimmunoprecipitation in MHCC97H cells overexpressing GFP-NT5DC2 or a GFP vector control. b Schematic graph showing the identification of EGFR and HSPD1 as potential NT5DC2-reacting proteins via LC-MS/MS and the HIPPIE database. c Western blot analysis of EGFR and HSPD1 expression in NT5DC2-overexpressing and NT5DC2-knockdown cells in both MHCC97H and PLC/RLF/5 cell lines (left). EGFR had higher expression in NT5DC2-overexpressing cell lines and lower expression in NT5DC2-knockdown cell lines (right, upper), while HSPD1 expression was unchanged in both NT5DC2-overexpressing and NT5DC2-knockdown cell lines (right, lower). d Coimmunoprecipitation assays were performed in MHCC97H and PLC/RLF/5 cells transfected with a vector containing GFP-tagged NT5DC2 or an empty vector. e Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed in PLC/RLF/5 cells, IgG was used as a control. Endogenous EGFR was co-immunoprecipitated by the anti-NT5DC2, while the endogenous NT5DC2 was reciprocally co-immunoprecipitated by the anti-EGFR antibody. f Co-localization of NT5DC2 (green) with EGFR (red) in PLC/RLF/5 cells on confocal microscopy. g NT5DC2 expression was determined via qPCR, while EGFR expression was determined via IHC (upper) in 79 human tumor tissues. EGFR expression was higher in the NT5DC2-high group (lower). h Slide sections were analyzed via IHC for EGFR expression in subcutaneous MHCC97H tumors (left). NT5DC2-overexpressing tumors had relatively higher EGFR scores, while NT5DC2 knockdown tumors had relatively lower EGFR scores on the IHC (right; magnification ×200). i Control or different NT5DC2 truncations with GFP tag were transfected into PLC/RLF/5 cells. Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed with anti-GFP beads.