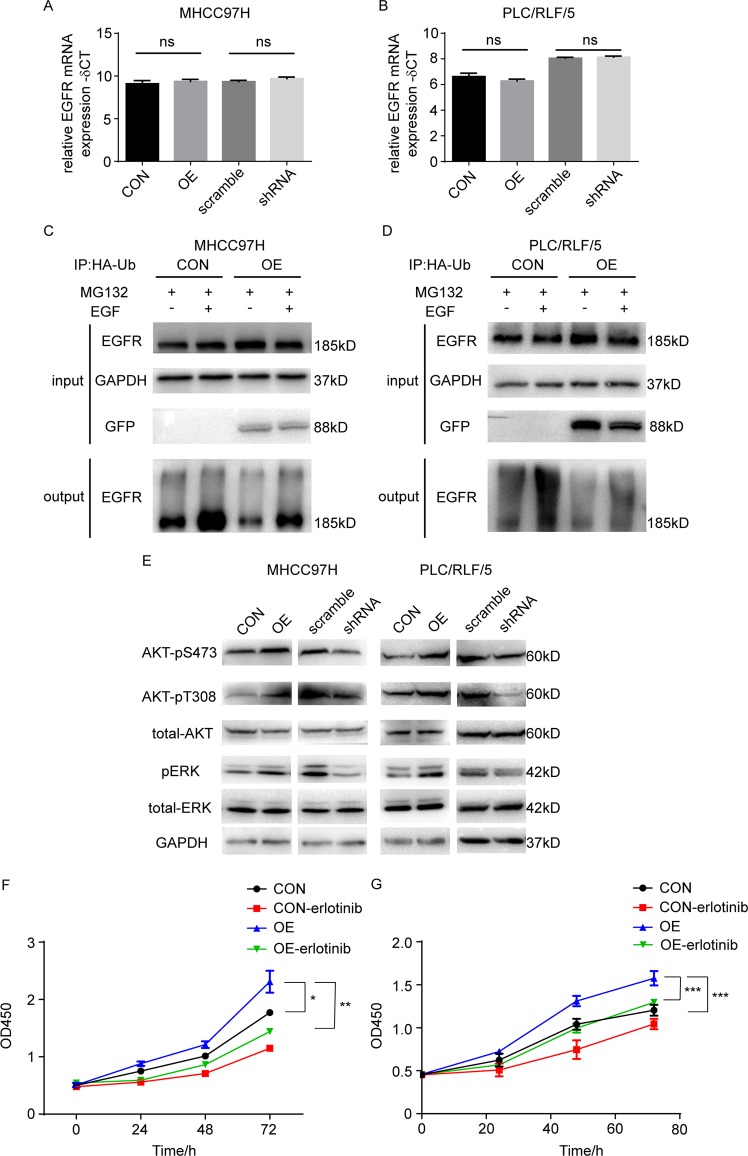
Fig. 5. NT5DC2 inhibited EGFR ubiquitin and promoted EGFR downstream signaling, while erlotinib blocked the effect of NT5DC2 on cell proliferation.
a, b qPCR analysis of EGFR mRNA levels in NT5DC2-overexpression and NT5DC2-knockdown cells in both MHCC97H (a) and PLC/RLF/5 (b) cell lines. c, d Western blot analysis of EGFR protein ubiquitination levels in MHCC97H cells (c) and PLC/RLF/5 cells treated with MG132 (10 μmol/L, 8 h) with or without EGF (25 ng/ml, 8 h) with the indicated antibodies. e Phosphorylation levels of EGFR signaling pathway-associated proteins, including AKT-pS473, AKT-pT308, and pERK, were detected via western blot in NT5DC2-overexpressing and NT5DC2-knockdown cells compared with their vector controls in both MHCC97H and PLC/RLF/5 cell lines. f, g CCK8 assays were performed to characterize the inhibitory effects of erlotinib on the proliferation of NT5DC2-overexpressing MHCC97H (f) and PLC/RLF/5 (g) cells.