Figure 2.

Novel re-analysis of TTI-621 binding and phagocytosis data from Ref. [72]. (A) Molecular partition function (ξ) fitting to the hemagglutination data. K1 and K2 are the association constants, inversely related to dissociation constants or EC50. Schematic of possible binding states of various CD47 affinity agents is shown for two apposed RBC membranes. Magrolimab (5F9) and BRIC126 both exhibit high hemagglutination and show cross-bridging, which can be fit (5F9: K1 = 1.2  10−2 nM−1, K2 = 0.24 nM−1; BRIC126: K1 = 6.6
10−2 nM−1, K2 = 0.24 nM−1; BRIC126: K1 = 6.6 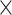 10−2 nM−1; K2 = 1.9 nM−1), whereas TTI-621, B6H12, and 2D3 do not. (B) TTI-621 shows non-zero binding to RBCs, which is weaker than anti-CD47 antibodies but consistent with past reports of sub-μM affinity between CD47 and SIRPα [39]. Inset: same data plotted with y-axis on log scale. Note that the plot follows the same color scheme as in (A). (C) TTI-621 binding data show sub-μM affinity for white blood cells, primary tumor samples, and human tumor cell lines. Phagocytosis of the human tumor lines requires less binding for effective phagocytosis. (D) TTI-621 binding affinities do not predict phagocytic efficiency across various cancer cell types. BR.C: breast cancer, AML: acute myeloid leukemia, BCL: B cell lymphoma, MM: multiple myeloma, and TCL: T-cell lymphoma.
10−2 nM−1; K2 = 1.9 nM−1), whereas TTI-621, B6H12, and 2D3 do not. (B) TTI-621 shows non-zero binding to RBCs, which is weaker than anti-CD47 antibodies but consistent with past reports of sub-μM affinity between CD47 and SIRPα [39]. Inset: same data plotted with y-axis on log scale. Note that the plot follows the same color scheme as in (A). (C) TTI-621 binding data show sub-μM affinity for white blood cells, primary tumor samples, and human tumor cell lines. Phagocytosis of the human tumor lines requires less binding for effective phagocytosis. (D) TTI-621 binding affinities do not predict phagocytic efficiency across various cancer cell types. BR.C: breast cancer, AML: acute myeloid leukemia, BCL: B cell lymphoma, MM: multiple myeloma, and TCL: T-cell lymphoma.
