Fig 2. Effects toxin-antitoxin modules, (p)ppGpp biosynthetic and degradation genes, or acidic pH on Salmonella persistence.
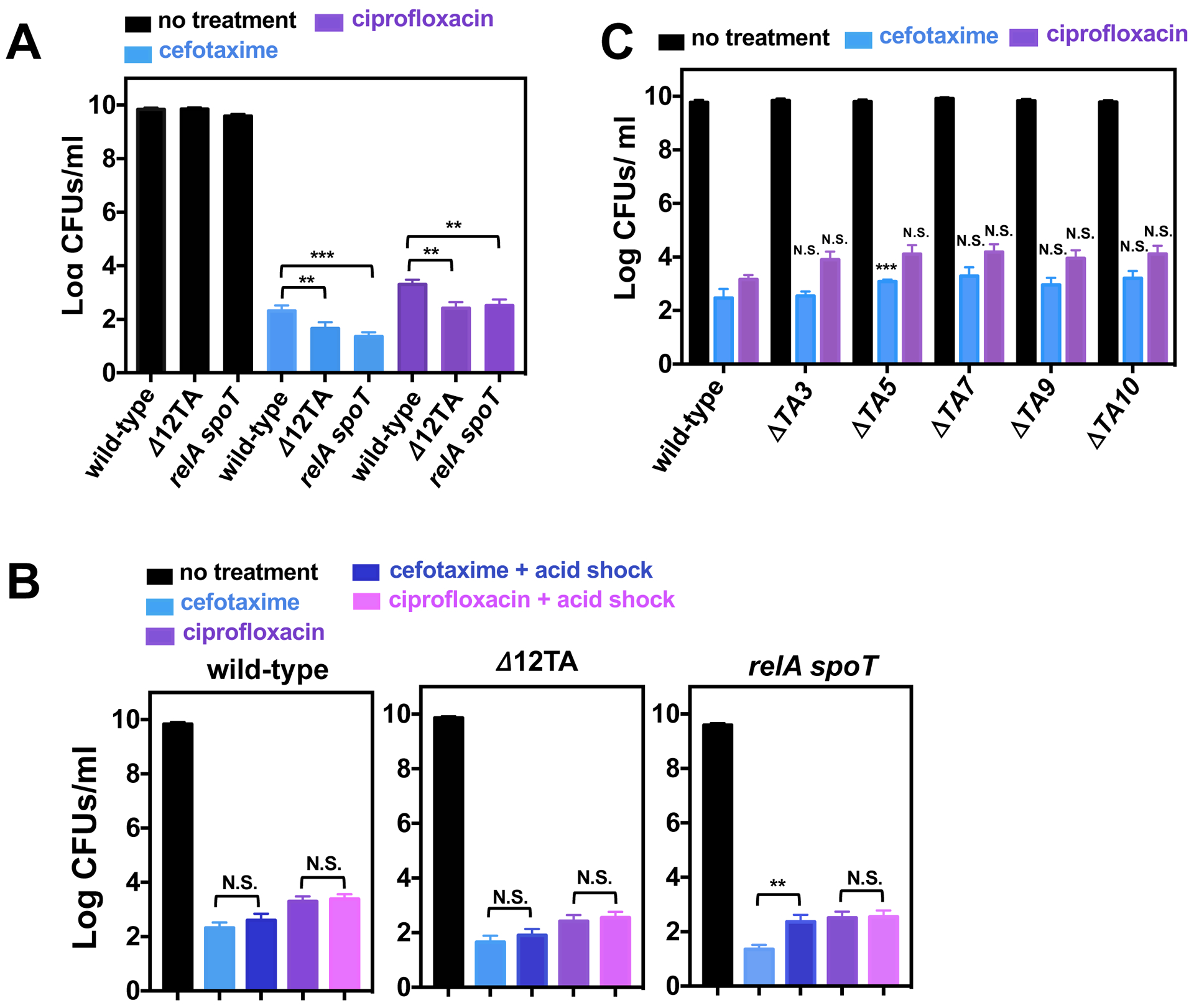
(A) Quantification of surviving wild-type (14028s), Δ12TA (MP1422), and relA::Tn10 spoT (MP342) Salmonella following 24 h exposure to cefotaxime or ciprofloxacin in LB medium. (B) Quantification of surviving wild-type (14028s), Δ12TA (MP1422), and relA::Tn10 spoT (MP342) Salmonella following acid shock (30 min in LB pH 4.5) prior to a 24 h exposure to cefotaxime or ciprofloxacin in LB medium. (C) Quantification of surviving wild-type (14028s), ΔTA3 (MP1454), ΔTA5 (MP1455), ΔTA7 (MP1456), ΔTA9 (MP1457), and ΔTA10 (MP1458) Salmonella following a 24 h exposure to cefotaxime or ciprofloxacin in LB medium. Error bars represent standard deviations (N = 8 biological replicates). Note log scale of y axis. For (A) and (B), two-tailed t-test between populations at the edge of brackets. For (C), two-tailed t-tests paired with wild-type populations: **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 and N.S. for no significance.
