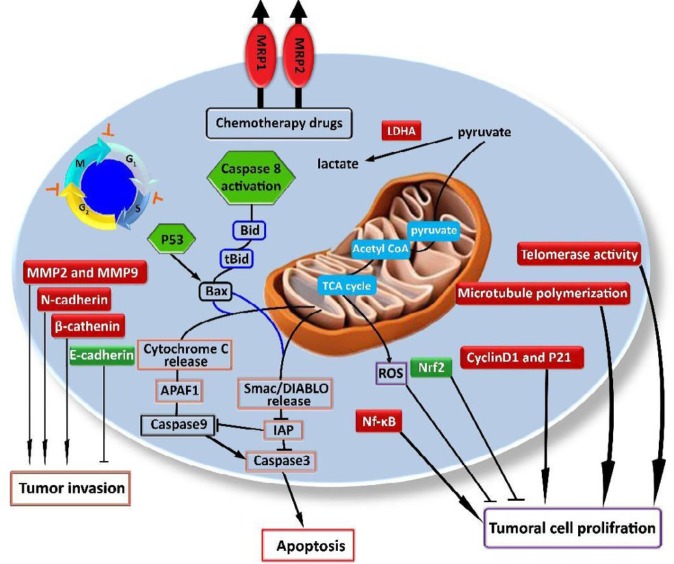
Figure 3.
Some important molecular mechanisms involved in the cytotoxic effect of crocin
Crocin inhibits telomerase activity, microtubule polymerization, cyclin D1 and p21 over expression, NF-kB expression and activation, and MRP1 and MRP2 expression contribute to tumor cell proliferation. Crocin also inhibits lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) and therefore causes increased production of mitochondrial ROS. Crocin can induce apoptosis through activation of caspase 8 and increasing p53 expression. It down-regulates matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 (MMP2 and MMP9), N-cadherin and beta-catenin expression, which are involved in tumor invasion and metastasis. Tumor invasion is inhibited by crocin through increasing E-cadherin expression. Cell cycle suppression at G1 and G0/G1 phases, S and G2/M phases are also induced by crocin in cancer cells. (legend of symbols: arrows indicate activation. truncated lines indicate inhibition. Red shapes indicate molecules or reactions down-regulated or inhibited by crocin. Green shapes indicate molecules or reactions up-regulated or activated by crocin. Short truncated orange lines around the cell cycle diagram indicate inhibition by crocin in certain phases)