Figure 4.
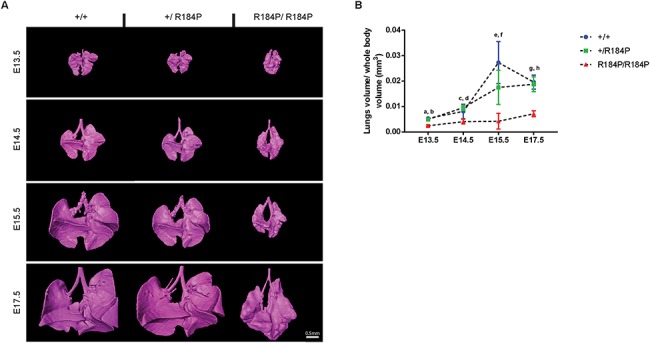
Analysis of lung development in R184P knock-in mouse model. (A) Lungs in the homozygous embryos were smaller and dysmorphic compared to heterozygous and wild-type lungs at all analysed stages. (B) Quantification of the 3D reconstructions of the lungs showed a significant decrease in lung volume of the homozygous embryos at all stages (n ≥ 12 per stage; a and b, P < 0.0001; c, P < 0.05; d, P < 0.0001; e and f, P < 0.01; g and h, P < 0.0001). Results are presented as mean ± SD.
