Figure 4.
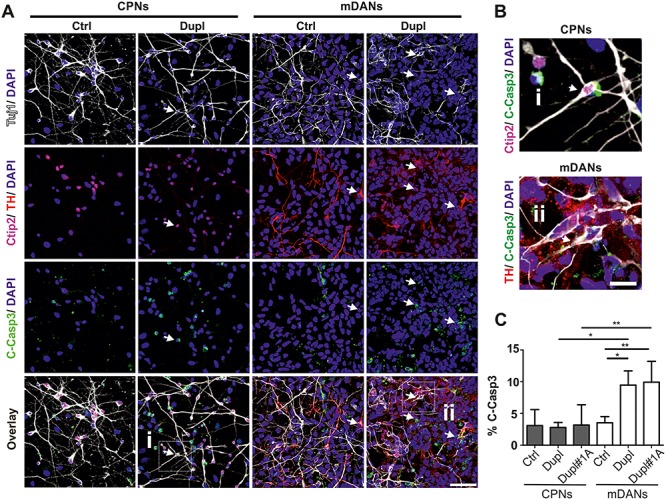
Increased apoptosis in mDANs compared with CPNs in PD Dupl cases. (A) iPSC-derived CPNs (Tuj1+/Ctip2+) and mDANs (Tuj1+/TH+) from the control individual (Ctrl) and PD Dupl patients (Dupl) were stained for cleaved Caspase-3 (C-Casp3) to determine neuronal death rate in respective neurons. Representative images used for neuronal subtype differentiation efficiency (Fig. 1B) and for the C-Casp3 (Fig. 4C) quantifications are shown. Arrows indicate the examples of C-Casp3+ neurons. (B) Enlarged views of selected cells marked by white frames in (A), representing a Tuj1+/Ctip2+/C-Casp3+ cell (i) and a Tuj1+/TH+/C-Casp3+ cells (ii). (C) Quantification of ICC analysis. iPSC-derived CPNs and mDANs from two PD Dupl patients (Dupl and Dupl#1A) were analyzed for neuronal cell death. Control (Ctrl) combines data from CPNs or mDANs, independently differentiated from two different iPSC clones of the same healthy individual. Significantly higher apoptosis rates were detected in mDANs from both PD Dupl patients (Dupl and Dupl#1A; % of TH+/C-Casp3+ over Tuj1+) compared with Ctrl, as well as to CPNs (% of Ctip2+/C-Casp3+ over Tuj1+) of PD Dupl cases. DAPI visualized cell nuclei. Values are shown as mean ± SD of three independent differentiations. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01 by one-way ANOVA. Scale bar 50 μm in (A) and 12.5 μm in (B).
