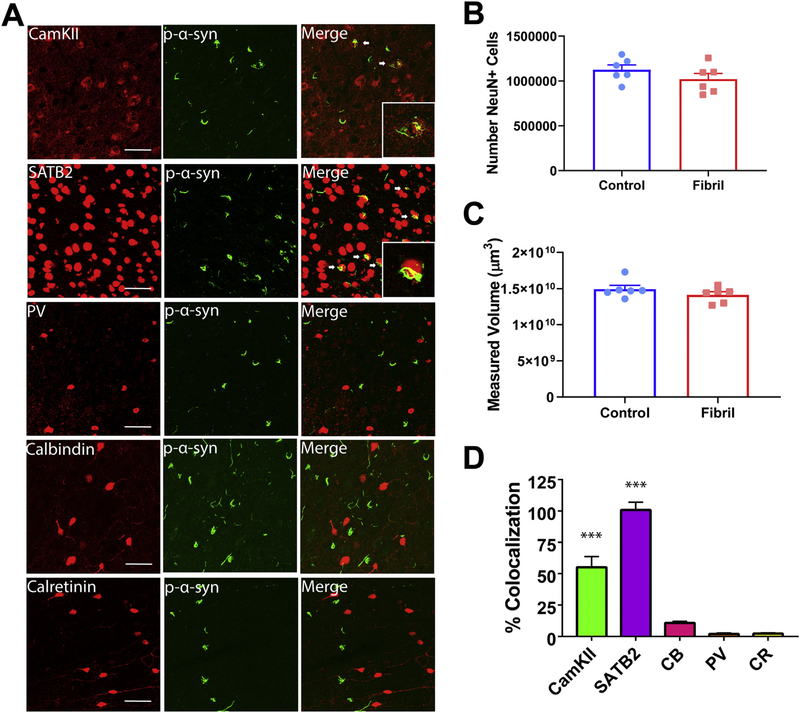
Fig. 6.
In the prefrontal cortex, p-α-synuclein inclusions localize primarily to excitatory neurons. Mice received bilateral injections of α-syn fibrils or monomeric α-synuclein as a control. A) Representative confocal images of excitatory and inhibitory markers (red) and pSer129-α-synuclein (green; EP1536Y used for costaining with CamKII, CB, and CR; 81a used for costaining with SATB2 and PV) in the prefrontal cortex. B) Unbiased volumetric estimation in the prefrontal cortex (N = 6/ group; unpaired t-test: p = .2542; t = 1.210; df = 10) C) Unbiased neuron count (N = 6/group; unpaired t-test: p = .2338; t = 1.267; df = 10). D) Quantification of colocalization of pSer129-α-synuclein over excitatory or inhibitory markers, normalized to pSer129-α-synuclein over NeuN (N = 3 with 3–5 images/mouse; ANOVA: p < .0001; F(4,40) = 81.54. ***p < .0001. Scale bar = 50 μm. Abbreviations: CR = calretinin, CamKII = Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, CB = calbindin, PV = parvalbumin. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)