Figure 3.
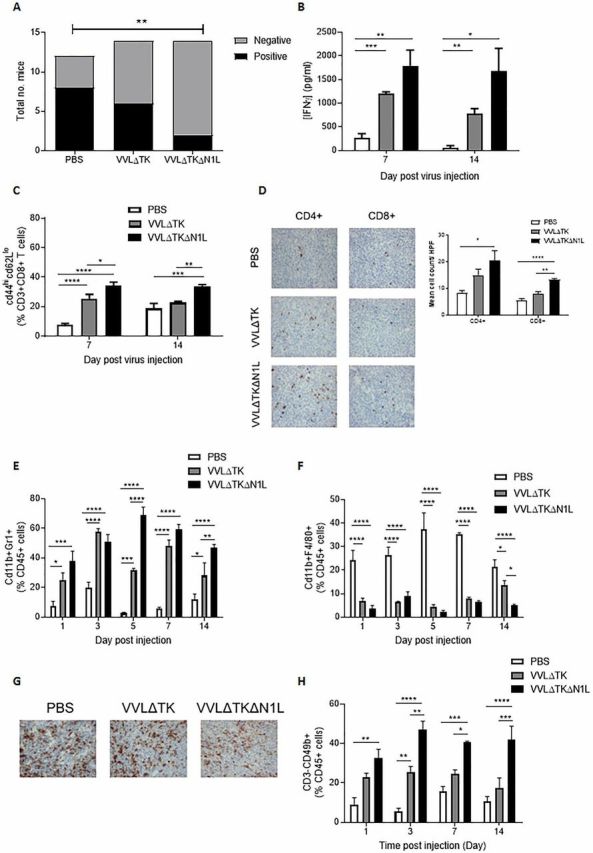
VVΔTKΔN1L induces adaptive and innate immunity against lung cancer in vivo. Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) tumors were established in the flanks of immune-competent C57/Bl6 mice. (A) Once palpable, mice were injected intratumorally (i.t) daily for 5 days with 1×108 PFU VVΔTK, VVΔTKΔN1L or PBS (n=14/group). Mice were sacrificed at day 15, lungs H&E stained and analyzed for the presence of metastasis by a pathologist blinded to treatment groups. Lungs were scored as negative or positive and a Fishers exact test used to determine significance. (B)–(H) Once palpable, mice were injected i.t once with 1×108 PFU VVΔTK, VVΔTKΔN1L or PBS (n=3–4/group). (B) Splenocytes were analyzed ex vivo for response to growth-arrested LLC cells using coculture for 72 hours followed by interferon γ (IFNγ) ELISA. (C) Splenocytes were collected and analyzed using FACS for expression of CD45, CD3, CD8, CD44 and CD62L. Percentage CD44hiCD62Llo cells (of live, CD45+/CD3+/CD8+ cells) are shown. (D) Tumors were collected 14 days post treatment and stained for CD4+ or CD8+ cells. Representative IHC images are shown (magnification x200) and cells/HPF shown graphically after 15 HPFs were counted. Of note, CD4+ staining cannot exclude the presence of TReg cells within the tumor. (E) FACS analysis was used to assess CD11b+Gr1+ neutrophils in tumors at the indicated time points. (F) FACS analysis was used to assess CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages in the tumors at the indicated time points. (G) Fourteen days post infection tumor sections were stained with F4/80 to assess macrophage infiltration. Representative images are shown. Magnification x200. (H) FACS analysis was used to assess CD3−CD49b+ natural killer cells in blood at the indicated time points. In all cases, one-way analysis of variance with post hoc Tukey tests was used to assess significance at each time point. In all cases, the mean±SEM is shown. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001.
