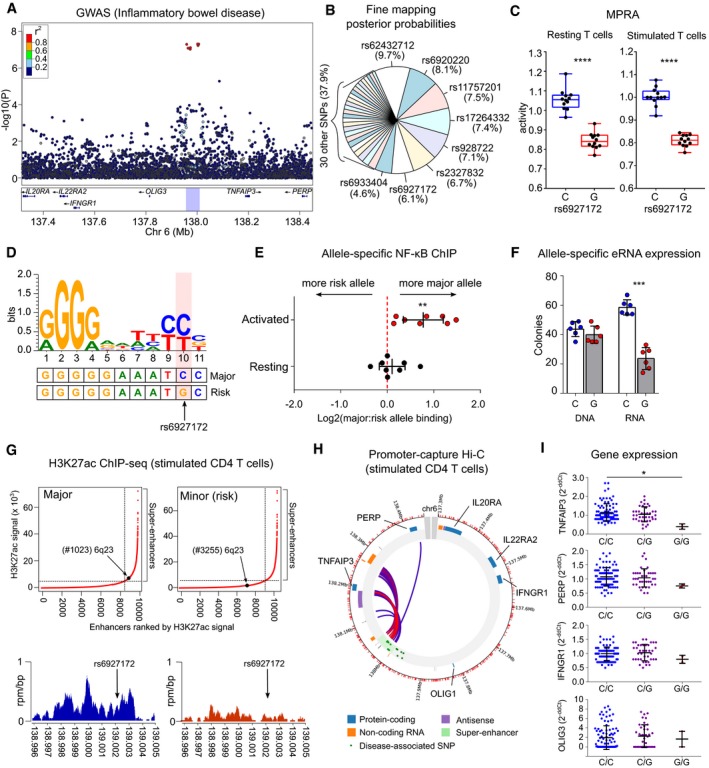
Figure 4. MPRA in CD4 T cells identifies an expression‐modulating variant that disrupts NF‐κB binding and enhancer function.
-
AIBD GWAS results (Liu et al, 2015) at a multi‐disease‐associated locus on chromosome 6q23.
-
BFine‐mapping results (Huang et al, 2017; posterior probabilities) for candidate SNPs at this locus.
-
CA single variant (rs6927172) has the largest and most significant expression‐modulating activity in resting (left panel) and stimulated CD4 T cells (right panel) with the risk allele reducing transcription. Plots represent median and IQR (box) and min to max (whiskers). FDR‐corrected meta‐analysis P value shown.
-
DSequence logo for an experimentally validated NF‐κB binding motif (Wong et al, 2011). The genomic sequence around rs6927172 is aligned below.
-
EAllele‐specific NF‐κB binding in CD4 T cells from rs6927172 heterozygotes, demonstrating reduced NF‐κB binding to the risk allele following stimulation (n = 8; one‐sample t‐test, two‐tailed).
-
FAllele‐specific expression of enhancer RNA in heterozygous CD4 T cells. DNA used for technical control (n = 6; paired t‐test; two‐tailed).
-
GGenome‐wide H3K27ac ChIP‐seq in stimulated CD4 T cells from major and minor allele homozygotes at rs6927172 (n = 6). Upper panels show input‐normalised H3K27ac signals plotted against enhancer rank. Super‐enhancers are defined above the inflection point of the curve. Lower panels show H3K27ac reads from a major (left) and a minor (risk) allele homozygote (right) in a 9 kb window around rs6927172.
-
HPromoter capture Hi‐C plot depicting interactions of the 6q23 super‐enhancer in stimulated CD4 T cells.
-
IExpression of genes on 6q23 in CD4 T cells from 131 patients with active IBD, stratified by rs6927172 genotype (qPCR; one‐way ANOVA). Error bars represent SD. Expression of IL20RA and IL22RAR2 not detected.
