Fig. 3. HDMP NPs recognize and transform into NFs on S. aureus in vitro.
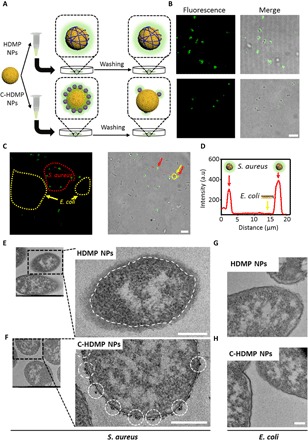
(A) Schematic illustration of HDMP NP– and C-HDMP NP–treated bacteria procedure. The bacteria were first treated with HDMP (30 μM) or C-HDMP (30 μM) NPs for 4 hours, followed by washing with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for confocal imaging. (B) Confocal microscopy showing specific recognition of HDMP NPs to S. aureus (top) and low targeting of C-HDMP to S. aureus (bottom). Scale bar, 5 μm. (C) Confocal imaging of S. aureus and E. coli mixture treated by the HDMP NPs (30 μM), showing the specific recognition of HDMP NPs to S. aureus, not E. coli. The red and yellow arrows indicate S. aureus and E. coli, respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) The normalized intensity profile for regions of interest across the red line in (C). (E to H) TEM images of S. aureus and E. coli treated with HDMP NPs (30 μM) and C-HDMP NPs (30 μM), exhibiting transformed HDMP fibrous networks out of the S. aureus wall (white dashed line) (E) and remained C-HDMP NPs (white dashed circles) on the S. aureus wall (F); the E. coli only without HDMP (G) and C-HDMP NPs (H). Scale bar, 200 nm. The confocal images and TEM images are representative of three independent experiments.
