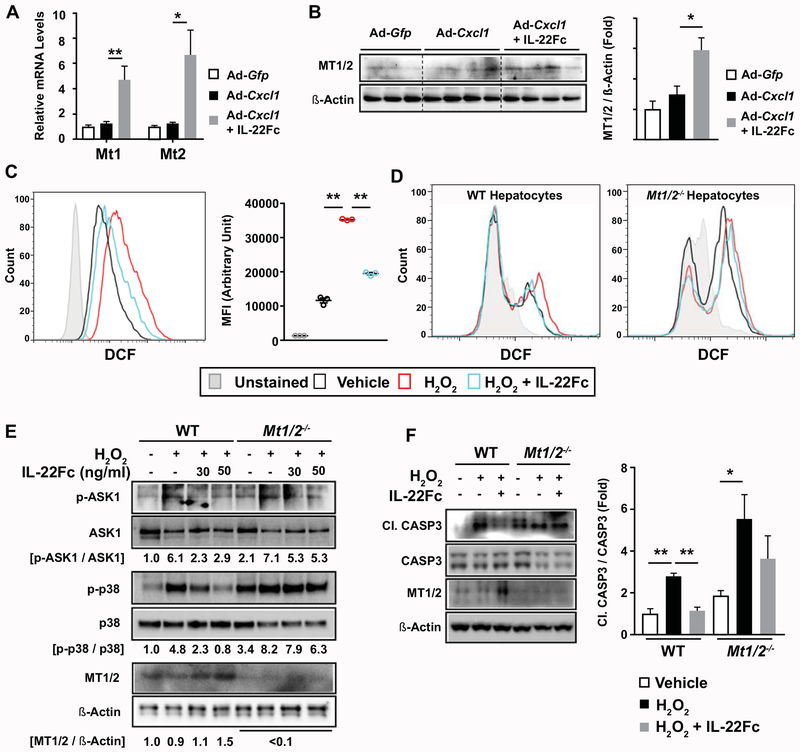
Fig. 5. MT contributes to the ability of IL-22Fc to attenuate ROS levels, stress kinase activation, and apoptotic signaling in hepatocytes.
(A, B) HFD-fed C57BL/6 mice were given Ad-Gfp, Ad-Cxcl1, or Ad-Cxcl1 + IL-22Fc (n=4-6/group). RT-qPCR (panel A) and immunoblot (panel B) analysis of hepatic mRNA and protein levels of Mt1 and Mt2, respectively. (C) AML12 cells were pretreated with IL-22Fc for 20 hr, exposed to H2O2 for 2 hr, and subjected to flow cytometric analysis of DCF. Results obtained from cells untreated with DCFDA dye represent the unstained condition. MFI represents the mean fluorescence intensity of triplicates. (D-F) Primary WT and Mt1/2−/− hepatocytes were pretreated with IL-22Fc for 20 hr, followed by a treatment with H2O2 for 30 min (panel D), 10 min (panel E), and 5 hr (panel F). ROS was measured by flow cytometric analysis of DCF (panel D). Immunoblot analyses were performed (panels E, F). Quantification of the CASP3 cleavage normalized to intact CASP3 from three independent experiments are shown in panel F (right). Values represent mean ± SEM. Statistical evaluation was performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons (*p<0.05; **p<0.01).