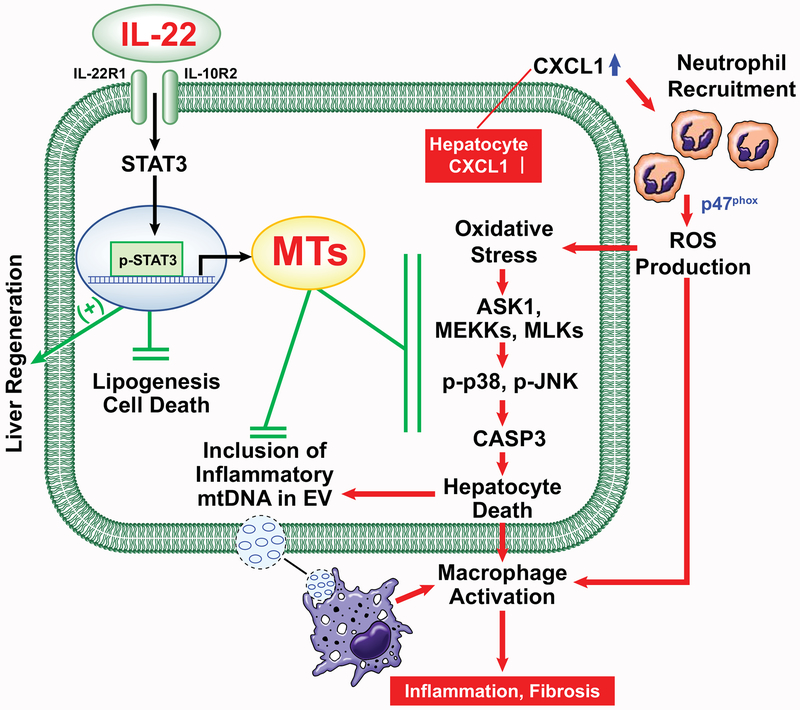
Fig. 8. A model depicting the therapeutic intervention of neutrophil-driven NASH by IL-22Fc that acts on multiple targets.
Adenoviral overexpression of CXCL1 in hepatocytes stimulates hepatic neutrophil infiltration and ROS production in a p47phox-dependent manner, which activates ROS-sensitive kinases (ASK1, MEKKs, and MLKs) and their downstream stress kinases (p38 and JNK) and subsequently enhances apoptotic signaling involving CASP3 cleavage. ROS-damaged hepatocytes enhance inflammation by releasing mtDNA-including EVs that activate macrophages. IL-22Fc alleviates CXCL1-induced NASH by attenuating hepatocyte death, inflammation, and fibrosis through MT induction in addition to its MT-independent effects (e.g., liver regeneration and inhibition of lipogenesis and cell death).