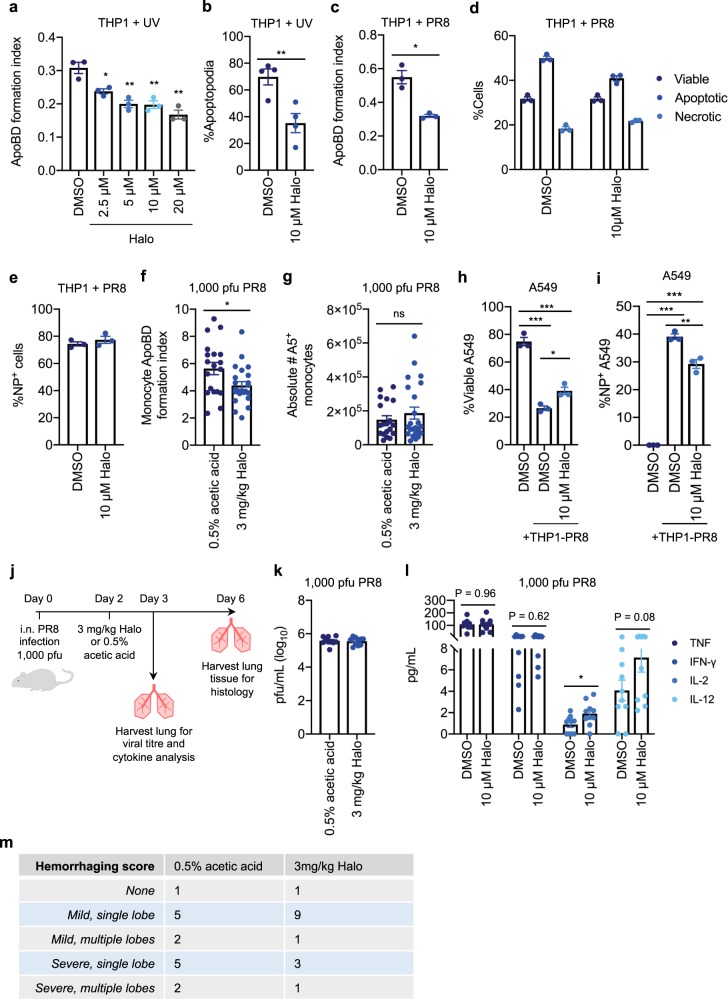
Fig. 6. Halo is a potent inhibitor of apoptotic cell disassembly and can limit viral propagation via ApoBDs.
a UV-irradiated THP1 monocytes were treated with 2.5–20 µM Halo for 4 h and the ApoBD formation index was determined by flow cytometry. b UV-irradiated THP1 monocytes were monitored by time-lapse DIC microscopy for 4 h in the presence of DMSO or 10 µM Halo and the percentage of cells forming apoptopodia was quantified (n = 4 independent experiments). THP1 monocytes were infected with PR8 for 24 h in the presence of DMSO or 10 µM Halo, and flow cytometry was performed to quantify the: c ApoBD formation index, d levels of viable, apoptotic, and necrotic cells, and e percentage of NP+ cells. PR8-infected (1000 pfu) mice were treated with either 0.5% acetic acid (vehicle control) or 3 mg/kg Halo on day 2 p.i. for 24 h, and flow cytometry was performed to quantify the monocyte ApoBD formation index (number of A5+ ApoBDs/number of A5+ cells) f, and the total number of A5+ monocytes within the BAL g (control n = 18 and Halo treatment n = 24 mice). PR8-infected THP1 monocytes were incubated with viable A549 epithelial cells for 48 h in the presence of DMSO or 10 µM Halo, and flow cytometry was performed to quantify the percentage of viable A549 cells h and percentage of NP+ A549 cells i. j Schematic of in vivo infection mouse model. Mice were infected with 1000 pfu PR8 and treated with 0.5% acetic acid or 3 mg/kg Halo on day 2 p.i., and lungs were harvested on day 3 p.i for viral titre (k, n = 10 mice) and cytokine analysis (l, n = 10 mice), or on day 6 p.i. for histological analysis (m, n = 13-14 mice). Histology slides were scored blind to determine the level of tissue haemorrhaging. Unless otherwise specified, error bars represent SEM of n = 3 biological repeats, presented data are representative of at least three independent experiments, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s two-tailed t-test.