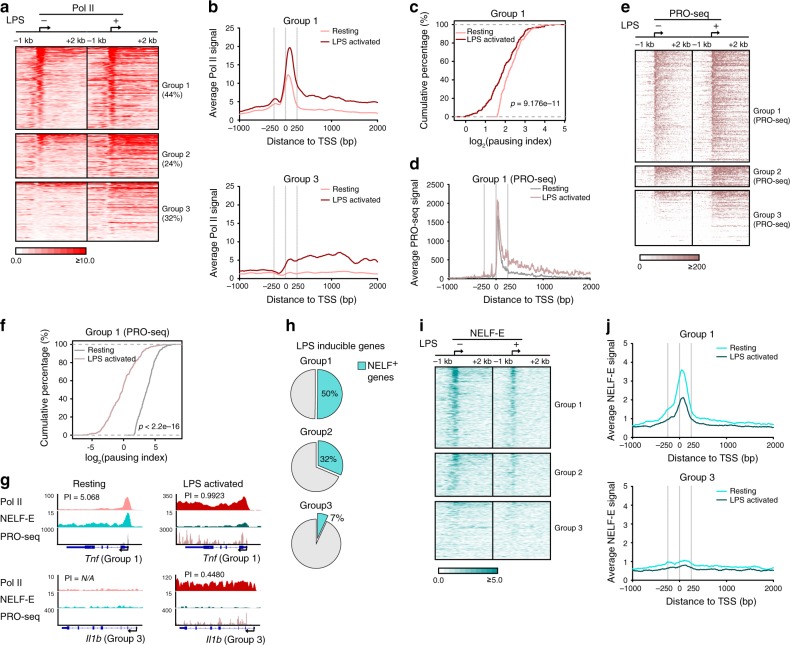
Fig. 3. Macrophage activation is associated with Pol II pause-release.
a Heat map of Pol II ChIP-seq signals in resting and LPS-activated (1 h) BMDM around the TSS regions of group 1–3 LPS-inducible genes. For each group, the rows were sorted by the decreasing Pol II ChIP-seq signal in the TSS region in resting BMDM. b Average Pol II ChIP-seq signals in resting and LPS-activated BMDM around TSS of group 1 (top) and group 3 (bottom) LPS-inducible genes. (c) The empirical cumulative distribution function (ECDF) plot of Pol II PI distribution of group 1 LPS-inducible genes in resting and LPS-activated BMDM. p Value (resting/LPS activated p = 9.176e−11) was calculated by two-sided Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. d Average PRO-seq signals (sense strand) in resting and LPS-activated BMDM around TSS of PRO-seq group 1 LPS-inducible genes. e Heat map of PRO-seq signals (sense strand) in resting and LPS-activated (0.5 h) BMDM around the TSS regions of group 1–3 LPS-inducible genes that were classified by PRO-seq defined PI. For each group, the rows were sorted by decreasing PRO-seq signals (sense strand) in TSS regions. f The empirical cumulative distribution function (ECDF) plot of PRO-seq-defined PI of group 1 LPS-inducible genes in resting and LPS-activated (0.5 h) BMDM. p Value (resting/LPS activated P < 2.2e−16) was calculated by two-sided Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. g Tracks of Pol II ChIP-seq, NELF-E ChIP-seq, and PRO-seq (sense strand), as indicated, are shown for representative group 1 (Tnf) and group 3 (Il1b) genes in resting (left) and LPS-activated (right) BMDM. h The percentage of NELF+ genes in group 1–3 of LPS-inducible genes. i Heat map of NELF-E ChIP-seq signals in resting and LPS-activated (0.5 h) BMDM around the TSS regions of group 1–3 LPS-inducible genes. For each group, the rows were sorted as in (a). j Average NELF-E ChIP-seq signals in resting and LPS-activated BMDM around TSS of group 1 (top) and group 3 (bottom) LPS-inducible genes.