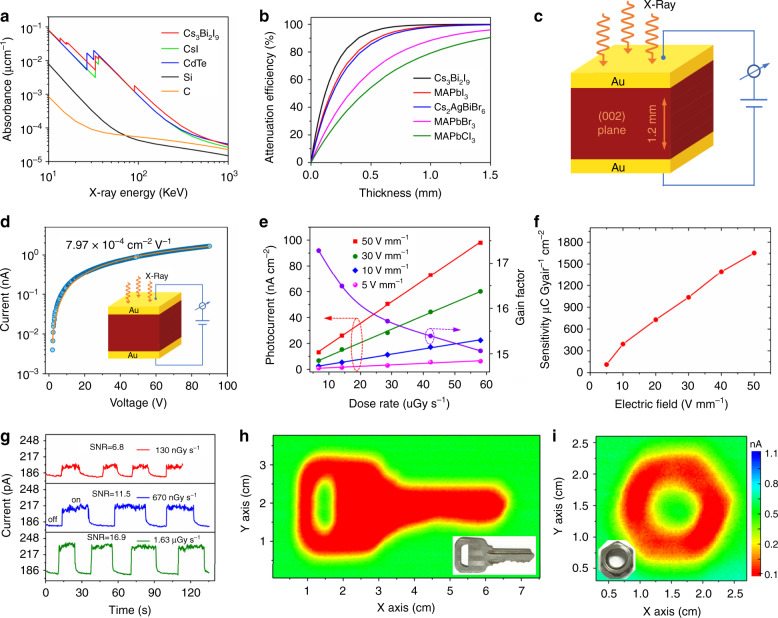
Fig. 5. Performance of Cs3Bi2I9 PSC X-ray detector and imaging.
a Absorption coefficients of Cs3Bi2I9, CsI, CdTe, silicon, and carbon as a function of photon energy. b Attenuation efficiency of Cs3Bi2I9, MAPbI3, Cs2AgBiBr6, MAPbBr3, MAPbCl3, silicon, and carbon for 40 keV X-ray photons versus thickness. c Schematic of the Cs3Bi2I9 PSC-based X-ray detector structure. d Photoconductivity measurement of the Cs3Bi2I9 PSC device with the inset illustrating the device structure. e X-ray-generated photocurrent density and gain factor versus dose rate under different applied biases. f Sensitivity under different electric field of the Cs3Bi2I9 PSC X-ray detector. g X-ray photocurrent response of the Cs3Bi2I9 PSC device under electric field of 50 V mm−1 when exposed to different X-ray dose rates. h, i Photos and corresponding X-ray images of a key and a nut obtained using the Cs3Bi2I9 SC detector (1 × 1 mm2), as measured under 50 V mm−1 electric field with dose rate of 36.2 µGyair s−1.